Deep Learning (09) - CNN / CIFAR-10
컨볼루션 신경망
CIFAR-10 살펴보기
데이터 살펴보기
In [1]:
from keras.datasets import cifar10
In [2]:
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = cifar10.load_data()
Out [2]:
Downloading data from https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz
170498071/170498071 [==============================] - 2s 0us/step
In [3]:
x_train.shape, y_train.shape
Out [3]:
((50000, 32, 32, 3), (50000, 1))
In [4]:
y_train[0] # 카테고리화 필요
Out [4]:
array([6], dtype=uint8)
In [5]:
x_train.min(), x_train.max() # 범위 조절 필요
Out [5]:
(0, 255)
- CIFAR-10 데이터 그려보기
In [6]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(777)
In [7]:
class_names = ['airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat',
'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse',
'ship', 'truck']
In [8]:
sample_size = 9
random_idx = np.random.randint(50000, size=sample_size)
In [9]:
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
for i, idx in enumerate(random_idx):
plt.subplot(3, 3, i+1)
plt.xticks([]) # 눈금 삭제
plt.yticks([]) # 눈금 삭제
plt.imshow(x_train[idx])
plt.xlabel(class_names[int(y_train[idx])])
plt.show()
Out [9]:

- 데이터 전처리
In [10]:
# 평균0 표준편차1인 정규분포로 변환
# 평균과 표준편차는 채널별로 구함
x_mean = np.mean(x_train, axis=(0, 1, 2))
x_std = np.std(x_train, axis=(0, 1, 2))
# x_train 기준
x_train = (x_train - x_mean) / x_std
x_test = (x_test - x_mean) / x_std
In [11]:
x_train.min(), x_train.max()
Out [11]:
(-1.98921279913639, 2.1267894095169213)
In [12]:
np.round(np.mean(x_train), 2)
Out [12]:
0.0
In [13]:
np.round(np.std(x_train), 2)
Out [13]:
1.0
In [14]:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
In [15]:
# 검증 데이터 분리
x_train, x_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(x_train, y_train, test_size=0.3, random_state=777)
In [16]:
x_train.shape, x_val.shape
Out [16]:
((35000, 32, 32, 3), (15000, 32, 32, 3))
In [17]:
# 손실함수를 sparse_categorical_crossentropy로 지정하면 레이블 원-핫 인코딩이 필요 없음
# from keras.utils import to_categorical
# y_train = to_categorical(y_train)
# y_test = to_categorical(y_test)
모델 구성하기
In [18]:
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Dense, Flatten
from keras.optimizers import Adam
In [19]:
# (32, 32, 3)의 데이터를 입력받음
model = Sequential([
Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu', input_shape=(32, 32, 3)),
Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=2, padding='same'),
Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=2, padding='same'),
Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'),
MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=2, padding='same'),
Flatten(),
Dense(256, activation='relu'),
Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(1e-4), # 학습률 0.0001로 지정
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['acc'])
모델 학습하기
In [20]:
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=30,
batch_size=32, validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
Out [20]:
Epoch 1/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 17s 7ms/step - loss: 1.6114 - acc: 0.4188 - val_loss: 1.4010 - val_acc: 0.4950
Epoch 2/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 7ms/step - loss: 1.2550 - acc: 0.5530 - val_loss: 1.2049 - val_acc: 0.5715
Epoch 3/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 1.0781 - acc: 0.6198 - val_loss: 1.0371 - val_acc: 0.6316
Epoch 4/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.9511 - acc: 0.6672 - val_loss: 0.9648 - val_acc: 0.6568
Epoch 5/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.8559 - acc: 0.7037 - val_loss: 0.9244 - val_acc: 0.6784
Epoch 6/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 8s 7ms/step - loss: 0.7733 - acc: 0.7326 - val_loss: 0.9081 - val_acc: 0.6803
Epoch 7/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.7021 - acc: 0.7568 - val_loss: 0.8680 - val_acc: 0.6993
Epoch 8/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 7ms/step - loss: 0.6293 - acc: 0.7827 - val_loss: 0.8186 - val_acc: 0.7185
Epoch 9/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.5643 - acc: 0.8077 - val_loss: 0.7965 - val_acc: 0.7255
Epoch 10/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.4942 - acc: 0.8296 - val_loss: 0.8020 - val_acc: 0.7345
Epoch 11/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.4339 - acc: 0.8504 - val_loss: 0.8154 - val_acc: 0.7341
Epoch 12/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.3772 - acc: 0.8706 - val_loss: 0.8469 - val_acc: 0.7357
Epoch 13/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.3164 - acc: 0.8932 - val_loss: 0.8981 - val_acc: 0.7353
Epoch 14/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.2641 - acc: 0.9114 - val_loss: 0.9414 - val_acc: 0.7311
Epoch 15/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.2174 - acc: 0.9264 - val_loss: 0.9825 - val_acc: 0.7328
Epoch 16/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.1726 - acc: 0.9431 - val_loss: 1.0559 - val_acc: 0.7345
Epoch 17/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.1393 - acc: 0.9525 - val_loss: 1.2586 - val_acc: 0.7155
Epoch 18/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.1121 - acc: 0.9626 - val_loss: 1.2563 - val_acc: 0.7325
Epoch 19/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0969 - acc: 0.9677 - val_loss: 1.3209 - val_acc: 0.7282
Epoch 20/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0858 - acc: 0.9719 - val_loss: 1.3294 - val_acc: 0.7332
Epoch 21/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0746 - acc: 0.9754 - val_loss: 1.3338 - val_acc: 0.7365
Epoch 22/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0656 - acc: 0.9783 - val_loss: 1.4120 - val_acc: 0.7326
Epoch 23/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0574 - acc: 0.9808 - val_loss: 1.5425 - val_acc: 0.7303
Epoch 24/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0554 - acc: 0.9811 - val_loss: 1.5385 - val_acc: 0.7303
Epoch 25/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0499 - acc: 0.9833 - val_loss: 1.5926 - val_acc: 0.7319
Epoch 26/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0472 - acc: 0.9841 - val_loss: 1.6220 - val_acc: 0.7323
Epoch 27/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0468 - acc: 0.9839 - val_loss: 1.6211 - val_acc: 0.7342
Epoch 28/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0445 - acc: 0.9843 - val_loss: 1.6731 - val_acc: 0.7319
Epoch 29/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0414 - acc: 0.9865 - val_loss: 1.7043 - val_acc: 0.7353
Epoch 30/30
1094/1094 [==============================] - 7s 6ms/step - loss: 0.0471 - acc: 0.9836 - val_loss: 1.6563 - val_acc: 0.7363
- 학습 과정 그려보기
In [21]:
his_dict = history.history
loss = his_dict['loss']
val_loss = his_dict['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(loss)+1)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
# 손실 그리기
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
ax1.plot(epochs, loss, color='blue', label='train_loss')
ax1.plot(epochs, val_loss, color='orange', label='val_loss')
ax1.set_title('train and val loss')
ax1.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax1.set_ylabel('loss')
ax1.legend()
acc = his_dict['acc']
val_acc = his_dict['val_acc']
# 정확도 그리기
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
ax2.plot(epochs, acc, color='blue', label='train_acc')
ax2.plot(epochs, val_acc, color='orange', label='val_acc')
ax2.set_title('train and val acc')
ax2.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax2.set_ylabel('loss')
ax2.legend()
Out [21]:
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f1cf00f9e80>
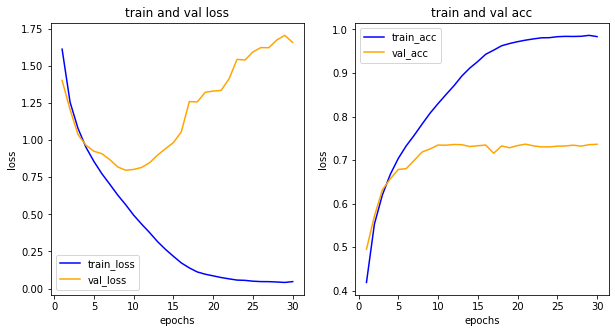
과대적합 문제가 발생!
- 신경망 시각화
In [22]:
import tensorflow as tf
In [23]:
get_layer_name = [layer.name for layer in model.layers] # 레이어를 하나씩 불러 이름을 저장
get_layer_name
Out [23]:
['conv2d',
'conv2d_1',
'max_pooling2d',
'conv2d_2',
'conv2d_3',
'max_pooling2d_1',
'conv2d_4',
'conv2d_5',
'max_pooling2d_2',
'flatten',
'dense',
'dense_1']
In [24]:
get_output = [layer.output for layer in model.layers] # 레이어를 통과해 나가는 데이터를 저장
get_output
Out [24]:
[<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 32, 32, 32) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'conv2d')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 32, 32, 32) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'conv2d_1')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 16, 16, 32) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'max_pooling2d')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 16, 16, 64) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'conv2d_2')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 16, 16, 64) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'conv2d_3')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 8, 8, 64) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'max_pooling2d_1')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 8, 8, 128) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'conv2d_4')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 8, 8, 128) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'conv2d_5')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 4, 4, 128) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'max_pooling2d_2')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 2048) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'flatten')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 256) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'dense')>,
<KerasTensor: shape=(None, 10) dtype=float32 (created by layer 'dense_1')>]
In [25]:
x_test[1].shape
Out [25]:
(32, 32, 3)
In [26]:
# 새로운 모델 생성
visual_model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=model.input, outputs=get_output)
# 모델에 넣어볼 데이터 가공
test_img = np.expand_dims(x_test[1], axis=0) # expand_dims: 차원 확장, axis=0 이므로 맨 앞에
In [27]:
test_img.shape
Out [27]:
(1, 32, 32, 3)
In [28]:
feature_maps = visual_model.predict(test_img)
Out [28]:
1/1 [==============================] - 0s 210ms/step
In [29]:
for layer_name, feature_map in zip(get_layer_name, feature_maps):
# Dense층 제외
if len(feature_map.shape) == 4: # 4차원인지 확인(Flatten층부터는 1차원으로 펼처짐)
img_size = feature_map.shape[1] # 몇행인지
features = feature_map.shape[-1] # 초기채널수 -> 필터수!
display_grid = np.zeros((img_size, img_size*features))
# 각 특징맵을 display_grid 배열에 붙임
for i in range(features):
x = feature_map[0, :, :, i] # [첫번째, 행, 열, 특성맵] # 특성맵을 한장씩 가져옴
x -= x.mean()
x /= x.std()
x *= 64
x += 128
x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8') # 계산 후 값의 범위를 0과 255사이로 지정
display_grid[:, i*img_size : (i+1)*img_size] = x # 특성맵을 붙일 자리 지정
plt.figure(figsize=(features, 2+1./features))
plt.title(layer_name, fontsize=20)
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(display_grid, aspect='auto')
Out [29]:
<ipython-input-29-5fdf75f2ad7f>:13: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide
x /= x.std()


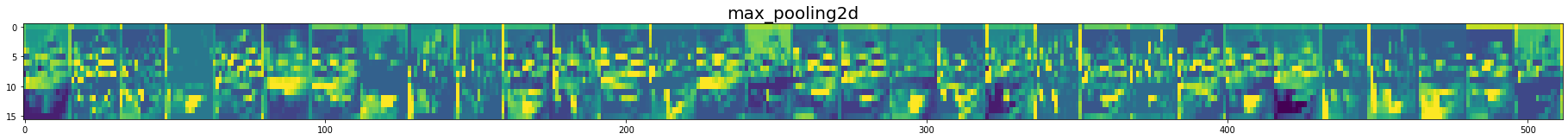

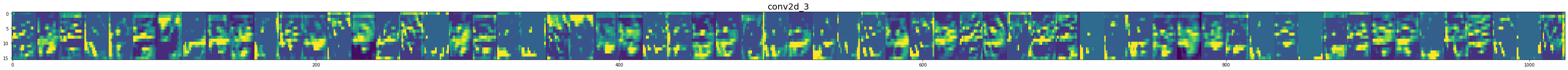




In [30]:
_, (x_test1, y_test1) = cifar10.load_data()
plt.imshow(x_test1[1])
Out [30]:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f1ca2112cd0>

Reference
- 이 포스트는 SeSAC 인공지능 자연어처리, 컴퓨터비전 기술을 활용한 응용 SW 개발자 양성 과정 - 심선조 강사님의 강의를 정리한 내용입니다.

댓글남기기