Machine Learning (9) - 결정 트리 실습
분류
결정 트리 실습
사용자 행동 인식(Human Activity Recognition) 데이터 세트
해당 데이터는 30명에게 스마트폰 센서를 장착한 뒤 사람의 동작과 관련된 여러가지 피처를 수집한 데이터이다.
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 피처 이름 불러오기, 구분자 \s+:공백 하나 이상
feature_name_df = pd.read_csv('human_activity/features.txt', sep='\s+',
header=None, names=['column_index', 'column_name'])
feature_name = feature_name_df.iloc[:, 1].values.tolist()
# feature_name_df['column_name'].values.tolist()[:10]
feature_name[:10]
['tBodyAcc-mean()-X',
'tBodyAcc-mean()-Y',
'tBodyAcc-mean()-Z',
'tBodyAcc-std()-X',
'tBodyAcc-std()-Y',
'tBodyAcc-std()-Z',
'tBodyAcc-mad()-X',
'tBodyAcc-mad()-Y',
'tBodyAcc-mad()-Z',
'tBodyAcc-max()-X']
# 중복된 피처명 조정
feature_dup_df = feature_name_df.groupby('column_name').count()
feature_dup_df[feature_dup_df['column_index'] > 1].count()
column_index 42
dtype: int64
feature_dup_df[feature_dup_df['column_index'] > 1].head(3)
| column_index | |
|---|---|
| column_name | |
| fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-1,16 | 3 |
| fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-1,24 | 3 |
| fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-1,8 | 3 |
def get_new_df(old_df):
dup_df = pd.DataFrame(data=old_df.groupby('column_name').cumcount(), columns=['dup_cnt']) # cumcount 그룹별로 묶어 같은값에 대해 번호를 매김
dup_df = dup_df.reset_index() # 기존의 인덱스값을 하나의 컬럼으로 추가
new_df = pd.merge(old_df.reset_index(), dup_df, how='outer') # reset_index하여 추가된 컬럼을 기준으로 병합
new_df['column_name'] = new_df[['column_name', 'dup_cnt']].apply(lambda x: x[0]+'_'+str(x[1]) if x[1]>0 else x[0], axis=1)
new_df.drop(columns=['index'], inplace=True)
return new_df
df = get_new_df(feature_name_df)
df[df['dup_cnt']>0]
| column_index | column_name | dup_cnt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | 317 | fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-1,8_1 | 1 |
| 317 | 318 | fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-9,16_1 | 1 |
| 318 | 319 | fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-17,24_1 | 1 |
| 319 | 320 | fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-25,32_1 | 1 |
| 320 | 321 | fBodyAcc-bandsEnergy()-33,40_1 | 1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 497 | 498 | fBodyGyro-bandsEnergy()-17,32_2 | 2 |
| 498 | 499 | fBodyGyro-bandsEnergy()-33,48_2 | 2 |
| 499 | 500 | fBodyGyro-bandsEnergy()-49,64_2 | 2 |
| 500 | 501 | fBodyGyro-bandsEnergy()-1,24_2 | 2 |
| 501 | 502 | fBodyGyro-bandsEnergy()-25,48_2 | 2 |
84 rows × 3 columns
def get_human_dataset():
# 데이터 파일 불러오기
feature_name_df = pd.read_csv('human_activity/features.txt', sep='\s+',
header=None, names=['column_index', 'column_name'])
# 중복 피처명 수정
name_df = get_new_df(feature_name_df)
# 피처명을 컬럼명으로 쓰기 위해 리스트로 추출
feature_name = name_df.iloc[:, 1].values.tolist()
# 학습 데이터와 테스트 데이터 불러오기, 컬럼명 feature_name으로 적용
X_train = pd.read_csv('human_activity/train/X_train.txt', sep='\s+', names=feature_name)
X_test = pd.read_csv('human_activity/test/X_test.txt', sep='\s+', names=feature_name)
# 학습 레이블과 테스트 레이블 불러오기, 컬럼명 action으로 적용
y_train = pd.read_csv('human_activity/train/y_train.txt', sep='\s+', names=['action'])
y_test = pd.read_csv('human_activity/test/y_test.txt', sep='\s+', names=['action'])
# 로드된 df반환
return X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = get_human_dataset()
X_train.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 7352 entries, 0 to 7351
Columns: 561 entries, tBodyAcc-mean()-X to angle(Z,gravityMean)
dtypes: float64(561)
memory usage: 31.5 MB
# 레이블 분포 확인
y_train['action'].value_counts()
6 1407
5 1374
4 1286
1 1226
2 1073
3 986
Name: action, dtype: int64
예측 분류 수행
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
dt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=156)
dt_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = dt_clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, pred)
print("결정 트리 예측 정확도 : {:.4f}".format(accuracy))
결정 트리 예측 정확도 : 0.8548
# 하이퍼 파라미터 확인
dt_clf.get_params()
{'ccp_alpha': 0.0,
'class_weight': None,
'criterion': 'gini',
'max_depth': None,
'max_features': None,
'max_leaf_nodes': None,
'min_impurity_decrease': 0.0,
'min_samples_leaf': 1,
'min_samples_split': 2,
'min_weight_fraction_leaf': 0.0,
'random_state': 156,
'splitter': 'best'}
하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
# 파라미터 하나에 대해 측정하고 다음 파라미터를 측정
params = {
'max_depth':[6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24],
'min_samples_split':[16]
}
# 교차 검증 5회 # 경우의 수 7*5=35가지
grid_cv = GridSearchCV(dt_clf, param_grid=params, scoring='accuracy', cv=5, verbose=1) # verbose default는 0, 오랜시간 수행할때 로그가 뜨는 정도
%%time
grid_cv.fit(X_train, y_train)
Fitting 5 folds for each of 7 candidates, totalling 35 fits
Wall time: 1min 48s
GridSearchCV(cv=5, estimator=DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=156),
param_grid={'max_depth': [6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24],
'min_samples_split': [16]},
scoring='accuracy', verbose=1)
print(f"GridSearchCV 최고 평균 정확도 : {grid_cv.best_score_:.4f}")
print(f"GridSearchCV 최적 하이퍼 파라미터 : {grid_cv.best_params_}")
GridSearchCV 최고 평균 정확도 : 0.8549
GridSearchCV 최적 하이퍼 파라미터 : {'max_depth': 8, 'min_samples_split': 16}
cv_result = pd.DataFrame(grid_cv.cv_results_)
cv_result[['param_max_depth', 'mean_test_score']]
| param_max_depth | mean_test_score | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 0.847662 |
| 1 | 8 | 0.854879 |
| 2 | 10 | 0.852705 |
| 3 | 12 | 0.845768 |
| 4 | 16 | 0.847127 |
| 5 | 20 | 0.848624 |
| 6 | 24 | 0.848624 |
# 별도의 테스트 데이터 세트에서 결정트리의 정확도 특정
max_depths = [6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 20, 24]
for depth in max_depths:
dt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=depth, min_samples_split=16, random_state=156)
dt_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = dt_clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, pred)
print(f"max_depth={depth} 정확도: {accuracy:.4f}")
max_depth=6 정확도: 0.8551
max_depth=8 정확도: 0.8717
max_depth=10 정확도: 0.8599
max_depth=12 정확도: 0.8571
max_depth=16 정확도: 0.8599
max_depth=20 정확도: 0.8565
max_depth=24 정확도: 0.8565
max_depth가 8일때 정확도가 가장 높다.
적절한 깊이를 지정해야 과적합을 방지할 수 있다!
# min_samples_split튜닝
params = {
'max_depth':[8],
'min_samples_split':[8, 12, 16, 20, 24]
}
grid_cv = GridSearchCV(dt_clf, param_grid=params, scoring='accuracy', cv=5, verbose=1)
%%time
grid_cv.fit(X_train, y_train)
Fitting 5 folds for each of 5 candidates, totalling 25 fits
Wall time: 1min 5s
GridSearchCV(cv=5,
estimator=DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=24,
min_samples_split=16,
random_state=156),
param_grid={'max_depth': [8],
'min_samples_split': [8, 12, 16, 20, 24]},
scoring='accuracy', verbose=1)
print(f"GridSearchCV 최고 평균 정확도 : {grid_cv.best_score_:.4f}")
print(f"GridSearchCV 최적 하이퍼 파라미터 : {grid_cv.best_params_}")
GridSearchCV 최고 평균 정확도 : 0.8549
GridSearchCV 최적 하이퍼 파라미터 : {'max_depth': 8, 'min_samples_split': 16}
pred = grid_cv.best_estimator_.predict(X_test)
print('최적 결정트리 예측 정확도 : {:.4f}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test, pred)))
최적 결정트리 예측 정확도 : 0.8717
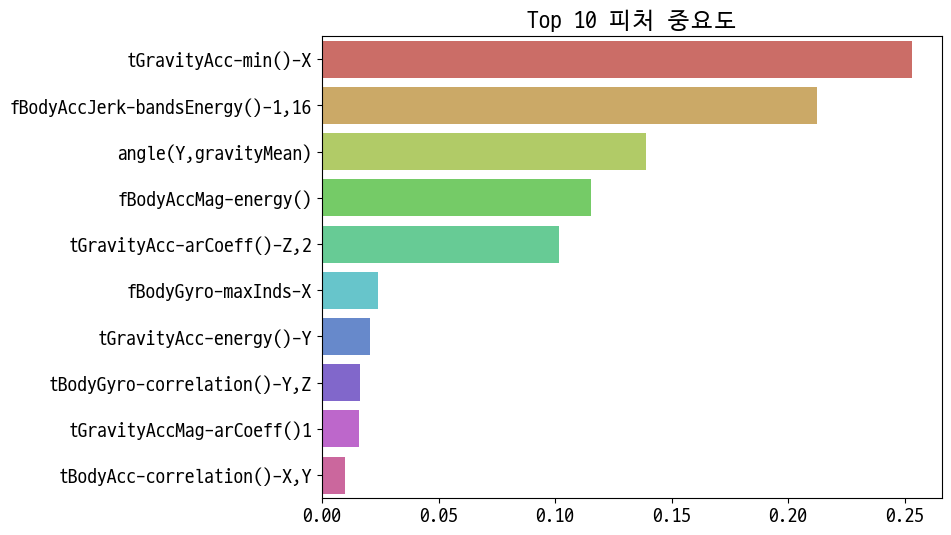
import seaborn as sns
data = pd.Series(grid_cv.best_estimator_.feature_importances_, index=X_train.columns)
top10 = data.sort_values(ascending=False)[:10]
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.title('Top 10 피처 중요도')
sns.barplot(x=top10, y=top10.index, palette='hls')
plt.show()
Reference
- 이 포스트는 SeSAC 인공지능 자연어처리, 컴퓨터비전 기술을 활용한 응용 SW 개발자 양성 과정 - 심선조 강사님의 강의를 정리한 내용입니다.
- Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphones Data Set

댓글남기기