Machine Learning (17) - 회귀 / 주택 가격
회귀
회귀 실습 - 주택 가격: 고급 회귀 기법
데이터 사전 처리(Preprocessing)
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
RMSLE로 평가
df = pd.read_csv('houseprice.csv')
df_org = df.copy()
df.head(2)
| Id | MSSubClass | MSZoning | LotFrontage | LotArea | Street | Alley | LotShape | LandContour | Utilities | ... | PoolArea | PoolQC | Fence | MiscFeature | MiscVal | MoSold | YrSold | SaleType | SaleCondition | SalePrice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 60 | RL | 65.0 | 8450 | Pave | NaN | Reg | Lvl | AllPub | ... | 0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0 | 2 | 2008 | WD | Normal | 208500 |
| 1 | 2 | 20 | RL | 80.0 | 9600 | Pave | NaN | Reg | Lvl | AllPub | ... | 0 | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0 | 5 | 2007 | WD | Normal | 181500 |
2 rows × 81 columns
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 1460 entries, 0 to 1459
Data columns (total 81 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Id 1460 non-null int64
1 MSSubClass 1460 non-null int64
2 MSZoning 1460 non-null object
3 LotFrontage 1201 non-null float64
4 LotArea 1460 non-null int64
5 Street 1460 non-null object
6 Alley 91 non-null object
7 LotShape 1460 non-null object
8 LandContour 1460 non-null object
9 Utilities 1460 non-null object
10 LotConfig 1460 non-null object
11 LandSlope 1460 non-null object
12 Neighborhood 1460 non-null object
13 Condition1 1460 non-null object
14 Condition2 1460 non-null object
15 BldgType 1460 non-null object
16 HouseStyle 1460 non-null object
17 OverallQual 1460 non-null int64
18 OverallCond 1460 non-null int64
19 YearBuilt 1460 non-null int64
20 YearRemodAdd 1460 non-null int64
21 RoofStyle 1460 non-null object
22 RoofMatl 1460 non-null object
23 Exterior1st 1460 non-null object
24 Exterior2nd 1460 non-null object
25 MasVnrType 1452 non-null object
26 MasVnrArea 1452 non-null float64
27 ExterQual 1460 non-null object
28 ExterCond 1460 non-null object
29 Foundation 1460 non-null object
30 BsmtQual 1423 non-null object
31 BsmtCond 1423 non-null object
32 BsmtExposure 1422 non-null object
33 BsmtFinType1 1423 non-null object
34 BsmtFinSF1 1460 non-null int64
35 BsmtFinType2 1422 non-null object
36 BsmtFinSF2 1460 non-null int64
37 BsmtUnfSF 1460 non-null int64
38 TotalBsmtSF 1460 non-null int64
39 Heating 1460 non-null object
40 HeatingQC 1460 non-null object
41 CentralAir 1460 non-null object
42 Electrical 1459 non-null object
43 1stFlrSF 1460 non-null int64
44 2ndFlrSF 1460 non-null int64
45 LowQualFinSF 1460 non-null int64
46 GrLivArea 1460 non-null int64
47 BsmtFullBath 1460 non-null int64
48 BsmtHalfBath 1460 non-null int64
49 FullBath 1460 non-null int64
50 HalfBath 1460 non-null int64
51 BedroomAbvGr 1460 non-null int64
52 KitchenAbvGr 1460 non-null int64
53 KitchenQual 1460 non-null object
54 TotRmsAbvGrd 1460 non-null int64
55 Functional 1460 non-null object
56 Fireplaces 1460 non-null int64
57 FireplaceQu 770 non-null object
58 GarageType 1379 non-null object
59 GarageYrBlt 1379 non-null float64
60 GarageFinish 1379 non-null object
61 GarageCars 1460 non-null int64
62 GarageArea 1460 non-null int64
63 GarageQual 1379 non-null object
64 GarageCond 1379 non-null object
65 PavedDrive 1460 non-null object
66 WoodDeckSF 1460 non-null int64
67 OpenPorchSF 1460 non-null int64
68 EnclosedPorch 1460 non-null int64
69 3SsnPorch 1460 non-null int64
70 ScreenPorch 1460 non-null int64
71 PoolArea 1460 non-null int64
72 PoolQC 7 non-null object
73 Fence 281 non-null object
74 MiscFeature 54 non-null object
75 MiscVal 1460 non-null int64
76 MoSold 1460 non-null int64
77 YrSold 1460 non-null int64
78 SaleType 1460 non-null object
79 SaleCondition 1460 non-null object
80 SalePrice 1460 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(35), object(43)
memory usage: 924.0+ KB
# null 값 확인
isnull_series = df.isnull().sum()
isnull_series[isnull_series > 0].sort_values(ascending=False)
PoolQC 1453
MiscFeature 1406
Alley 1369
Fence 1179
FireplaceQu 690
LotFrontage 259
GarageType 81
GarageYrBlt 81
GarageFinish 81
GarageQual 81
GarageCond 81
BsmtExposure 38
BsmtFinType2 38
BsmtFinType1 37
BsmtCond 37
BsmtQual 37
MasVnrArea 8
MasVnrType 8
Electrical 1
dtype: int64
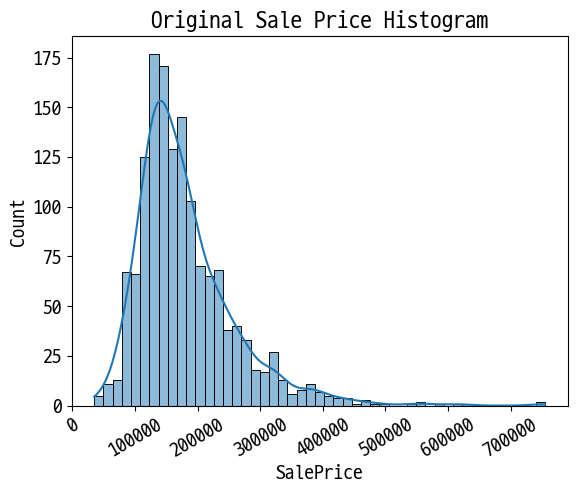
# 타깃 값의 분포 확인
plt.title('Original Sale Price Histogram')
plt.xticks(rotation=30)
sns.histplot(df['SalePrice'], kde=True)
plt.show()
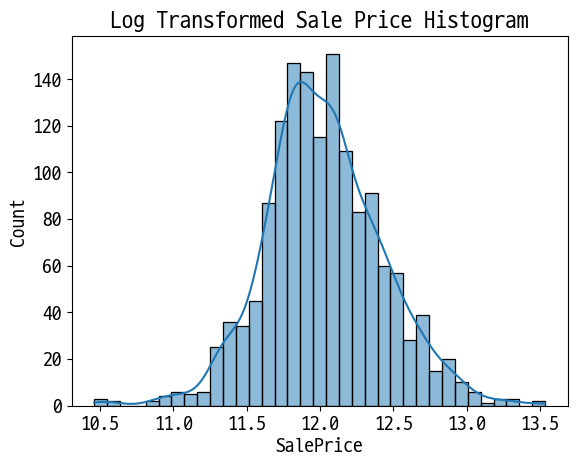
# 정규분포 형태로 변환 후 분포 확인
plt.title('Log Transformed Sale Price Histogram')
log_SalePrice = np.log1p(df['SalePrice'])
sns.histplot(log_SalePrice, kde=True)
plt.show()
# SalePrice 로그 변환
ori_SalePrice = df['SalePrice'] # 나중에 다시 확인할 용도로 백업
df['SalePrice'] = np.log1p(df['SalePrice'])
# Null이 많은 컬럼 5개, id 컬럼 제거
df.drop(columns=['Id', 'PoolQC', 'MiscFeature', 'Alley', 'Fence', 'FireplaceQu'], inplace=True)
# 숫자형 null은 평균값으로 대체
df.fillna(df.mean(), inplace=True)
# null이 남은 object형 확인
null_column_count = df.isnull().sum()[df.isnull().sum() > 0]
df.dtypes[null_column_count.index]
MasVnrType object
BsmtQual object
BsmtCond object
BsmtExposure object
BsmtFinType1 object
BsmtFinType2 object
Electrical object
GarageType object
GarageFinish object
GarageQual object
GarageCond object
dtype: object
# 문자형 원-핫 인코딩(Null도 같이 변환)
print('before:', df.shape)
df_ohe = pd.get_dummies(df)
print('after:', df_ohe.shape)
before: (1460, 75)
after: (1460, 271)
선형 회귀 모델 학습/예측/평가
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, Ridge, Lasso
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
def get_rmse(model):
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
import numpy as np
pred = model.predict(X_test)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, pred)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
print(f'{model.__class__.__name__} 로그 변환된 RMSE: {np.round(rmse, 3)}')
return rmse
def get_rmses(models):
rmses = []
for model in models:
rmse = get_rmse(model)
rmses.append(rmse)
return rmses
y = df_ohe['SalePrice']
X = df_ohe.drop(columns='SalePrice')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=156)
lr_reg = LinearRegression()
lr_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
ridge_reg = Ridge()
ridge_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
lasso_reg = Lasso()
lasso_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
models = [lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg]
get_rmses(models)
LinearRegression 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.132
Ridge 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.128
Lasso 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.176
[0.13189576579154494, 0.12750846334052998, 0.17628250556471403]
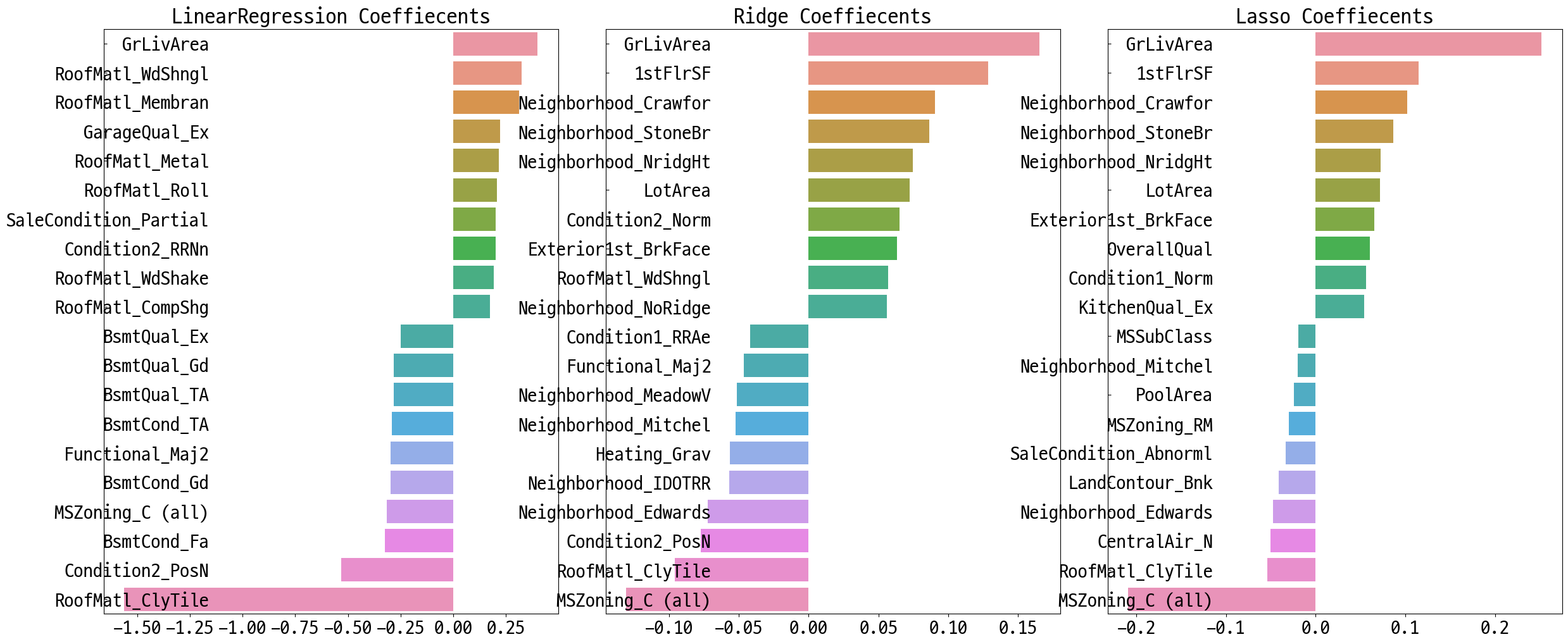
컬럼별 회귀 계수 확인
def get_top_bottom_coef(model, n=10):
coef = pd.Series(model.coef_, index=X.columns)
# 상위, 하위 n개씩 추출
coef_high = coef.sort_values(ascending=False).head(n)
coef_low = coef.sort_values(ascending=False).tail(n)
return coef_high, coef_low
def visualize_coef(models):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(figsize=(24,10), nrows=1, ncols=3)
fig.tight_layout() # plot배치를 정렬
for idx, model in enumerate(models):
coef_high, coef_low = get_top_bottom_coef(model)
coef_concat = pd.concat([coef_high , coef_low])
# ax subplot에 barchar로 표현. 한 화면에 표현하기 위해 tick label 위치와 font 크기 조정.
axs[idx].set_title(model.__class__.__name__+' Coeffiecents', size=25)
axs[idx].tick_params(axis='y', direction='in', pad=-120) # y축 tick을 -120만큼 안으로 들임
for label in (axs[idx].get_xticklabels() + axs[idx].get_yticklabels()):
label.set_fontsize(22)
sns.barplot(x=coef_concat.values, y=coef_concat.index , ax=axs[idx])
# 앞 예제에서 학습한 lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg 모델의 회귀 계수 시각화.
models = [lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg]
visualize_coef(models)
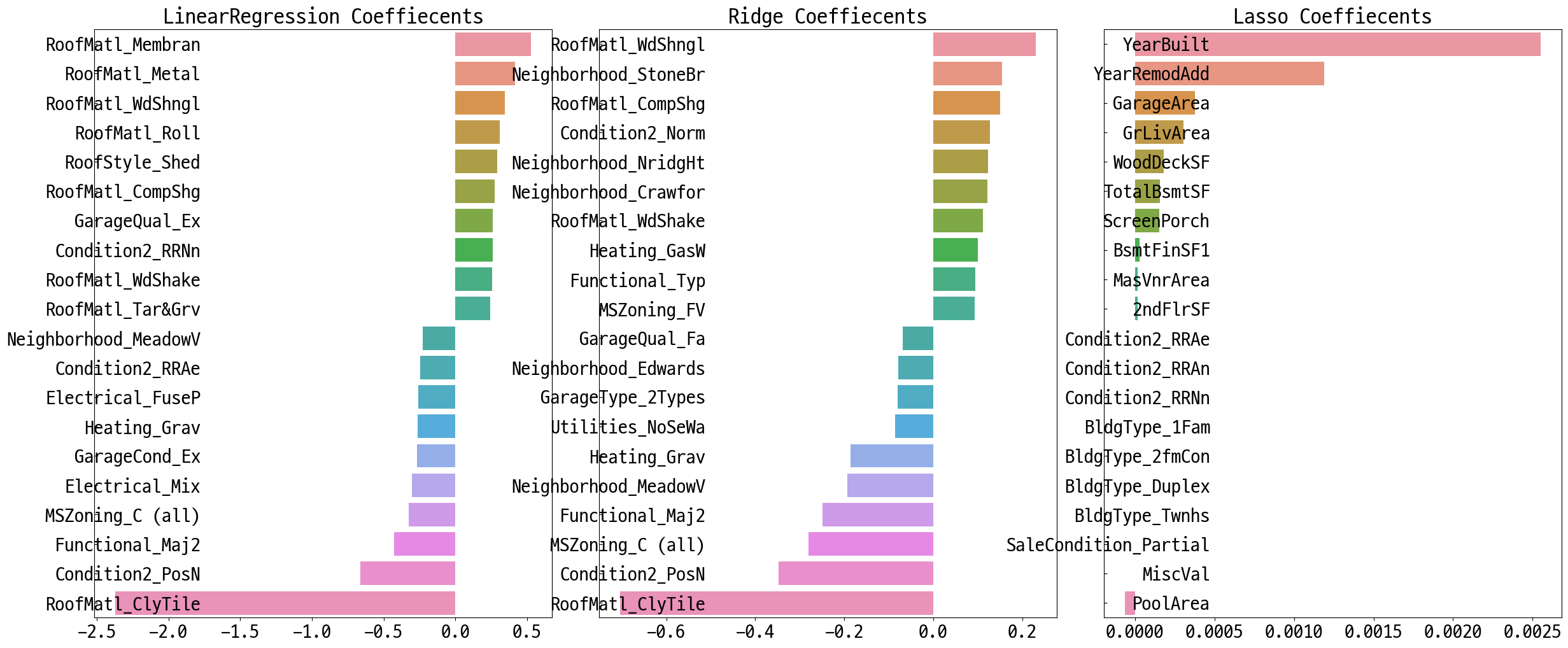
교차검증
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
def get_avg_rmse_cv(models):
for model in models:
# 분할하지 않고 전체 데이터로 cross_val_score() 수행. 모델별 CV RMSE값과 평균 RMSE 출력
rmse_list = np.sqrt(-cross_val_score(model, X, y,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv = 5))
rmse_avg = np.mean(rmse_list)
print(f'\n{model.__class__.__name__} CV RMSE 값 리스트: {np.round(rmse_list, 3)}')
print(f'{model.__class__.__name__} CV 평균 RMSE 값: {np.round(rmse_avg, 3)}')
models = [lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg]
get_avg_rmse_cv(models)
LinearRegression CV RMSE 값 리스트: [0.135 0.165 0.168 0.111 0.198]
LinearRegression CV 평균 RMSE 값: 0.155
Ridge CV RMSE 값 리스트: [0.117 0.154 0.142 0.117 0.189]
Ridge CV 평균 RMSE 값: 0.144
Lasso CV RMSE 값 리스트: [0.161 0.204 0.177 0.181 0.265]
Lasso CV 평균 RMSE 값: 0.198
하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
def print_best_params(model, params):
grid_model = GridSearchCV(model, param_grid=params, scoring='neg_mean_squared_error', cv=5)
grid_model.fit(X, y)
rmse = np.sqrt(-1*grid_model.best_score_)
print(f'{model.__class__.__name__} 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: {np.round(rmse, 4)}, 최적 alpha:{grid_model.best_params_}')
return grid_model.best_estimator_
ridge_params = {'alpha':[0.05, 0.1, 1, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20]}
lasso_params = {'alpha':[0.001, 0.005, 0.008, 0.05, 0.03, 0.1, 0.5, 1,5, 10]}
best_rige = print_best_params(ridge_reg, ridge_params)
best_lasso = print_best_params(lasso_reg, lasso_params)
Ridge 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1418, 최적 alpha:{'alpha': 12}
Lasso 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.142, 최적 alpha:{'alpha': 0.001}
lr_reg = LinearRegression()
lr_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
ridge_reg = Ridge(alpha=12)
ridge_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
lasso_reg = Lasso(alpha=0.001)
lasso_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
models = [lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg]
get_rmses(models)
visualize_coef(models)
LinearRegression 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.132
Ridge 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.124
Lasso 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.12
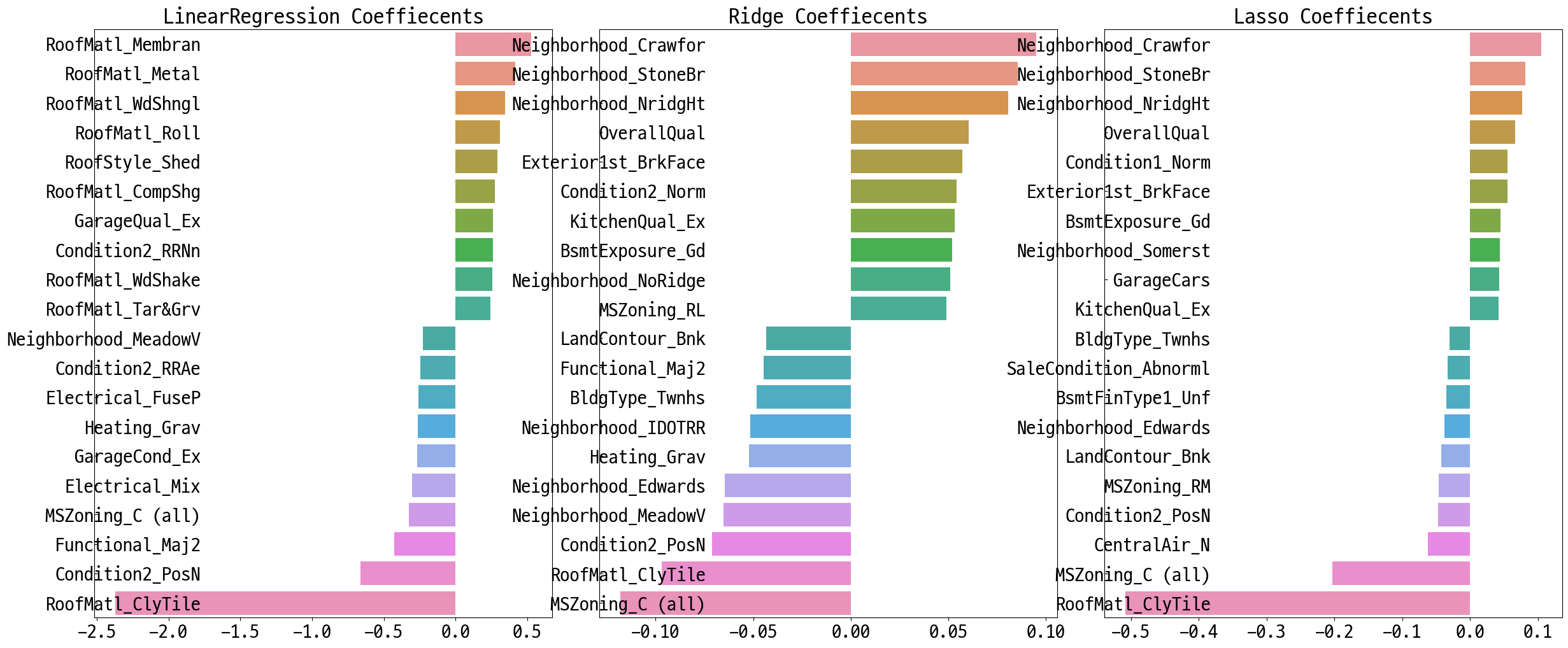
피처 데이터 왜곡 확인
from scipy.stats import skew
features_idx = df.dtypes[df.dtypes != 'object'].index
skew_features = df[features_idx].apply(lambda x: skew(x))
skew_features_top = skew_features[skew_features > 1]
print(skew_features_top.sort_values(ascending=False))
MiscVal 24.451640
PoolArea 14.813135
LotArea 12.195142
3SsnPorch 10.293752
LowQualFinSF 9.002080
KitchenAbvGr 4.483784
BsmtFinSF2 4.250888
ScreenPorch 4.117977
BsmtHalfBath 4.099186
EnclosedPorch 3.086696
MasVnrArea 2.673661
LotFrontage 2.382499
OpenPorchSF 2.361912
BsmtFinSF1 1.683771
WoodDeckSF 1.539792
TotalBsmtSF 1.522688
MSSubClass 1.406210
1stFlrSF 1.375342
GrLivArea 1.365156
dtype: float64
df[skew_features_top.index] = np.log1p(df[skew_features_top.index])
# 다시 원-핫-인코딩 후 데이터 세트 설정
df_ohe = pd.get_dummies(df)
y = df_ohe['SalePrice']
X = df_ohe.drop(columns='SalePrice')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=156)
# 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝
ridge_params = {'alpha':[0.05, 0.1, 1, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20]}
lasso_params = {'alpha':[0.001, 0.005, 0.008, 0.05, 0.03, 0.1, 0.5, 1,5, 10]}
best_rige = print_best_params(ridge_reg, ridge_params)
best_lasso = print_best_params(lasso_reg, lasso_params)
Ridge 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1275, 최적 alpha:{'alpha': 10}
Lasso 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1252, 최적 alpha:{'alpha': 0.001}
# 최적 튜닝값 적용, 컬럼별 회귀 계수 시각화
lr_reg = LinearRegression()
lr_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
ridge_reg = Ridge(alpha=10)
ridge_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
lasso_reg = Lasso(alpha=0.001)
lasso_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
models = [lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg]
get_rmses(models)
visualize_coef(models)
LinearRegression 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.128
Ridge 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.122
Lasso 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.119
이상치 확인과 삭제
종속 변수에 가장 영향을 주는 독립 변수의 이상치 제어
plt.scatter(x=df_org['GrLivArea'], y=df_org['SalePrice'])
plt.ylabel('SalePrice', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('GrLivArea', fontsize=15)
plt.show()
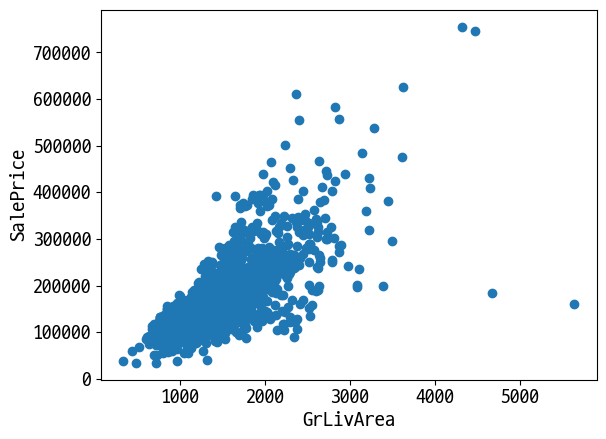
# GrLivArea와 SalePrice 로그 변환됏으므로 이를 반영
cond1 = df_ohe['GrLivArea'] > np.log1p(4000)
cond2 = df_ohe['SalePrice'] < np.log1p(500000)
outlier_idx = df_ohe[cond1 & cond2].index
print('이상치 index:', outlier_idx.values)
print('이상치 삭제 전 df_ohe.shape:', df_ohe.shape)
이상치 index: [ 523 1298]
이상치 삭제 전 df_ohe.shape: (1460, 271)
df_ohe.drop(index=outlier_idx, inplace=True)
print('이상치 삭제 후 df_ohe.shape:', df_ohe.shape)
이상치 삭제 후 df_ohe.shape: (1458, 271)
# 데이터 세트 재설정
y = df_ohe['SalePrice']
X = df_ohe.drop(columns='SalePrice')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=156)
# 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝
ridge_params = {'alpha':[0.05, 0.1, 1, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20]}
lasso_params = {'alpha':[0.001, 0.005, 0.008, 0.05, 0.03, 0.1, 0.5, 1,5, 10]}
best_rige = print_best_params(ridge_reg, ridge_params)
best_lasso = print_best_params(lasso_reg, lasso_params)
Ridge 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1125, 최적 alpha:{'alpha': 8}
Lasso 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1122, 최적 alpha:{'alpha': 0.001}
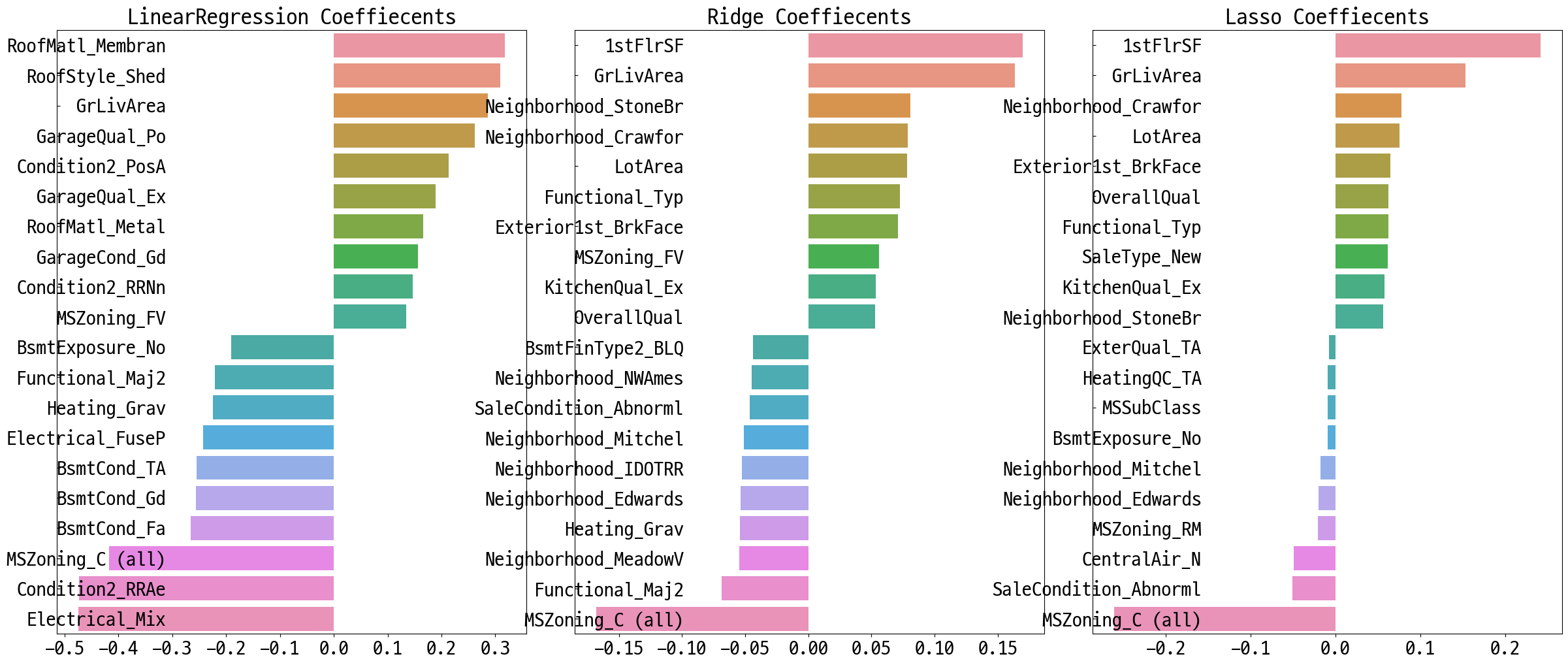
# 최적 튜닝값 적용, 컬럼별 회귀 계수 시각화
lr_reg = LinearRegression()
lr_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
ridge_reg = Ridge(alpha=8)
ridge_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
lasso_reg = Lasso(alpha=0.001)
lasso_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
models = [lr_reg, ridge_reg, lasso_reg]
get_rmses(models)
visualize_coef(models)
LinearRegression 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.129
Ridge 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.103
Lasso 로그 변환된 RMSE: 0.1
회귀 트리 모델 학습/예측/평가
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
xgb_params = {'n_estimators':[1000]}
xgb_reg = XGBRegressor(n_estimators=1000, learning_rate=0.05,
colsample_bytree=0.5, subsample=0.8)
best_xgb = print_best_params(xgb_reg, xgb_params)
XGBRegressor 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1178, 최적 alpha:{'n_estimators': 1000}
lgbm_params = {'n_estimators':[1000]}
lgbm_reg = LGBMRegressor(n_estimators=1000, learning_rate=0.05, num_leaves=4,
subsample=0.6, colsample_bytree=0.4, reg_lambda=10, n_jobs=-1)
best_lgbm = print_best_params(lgbm_reg, lgbm_params)
LGBMRegressor 5 CV 시 최적 평균 RMSE 값: 0.1163, 최적 alpha:{'n_estimators': 1000}
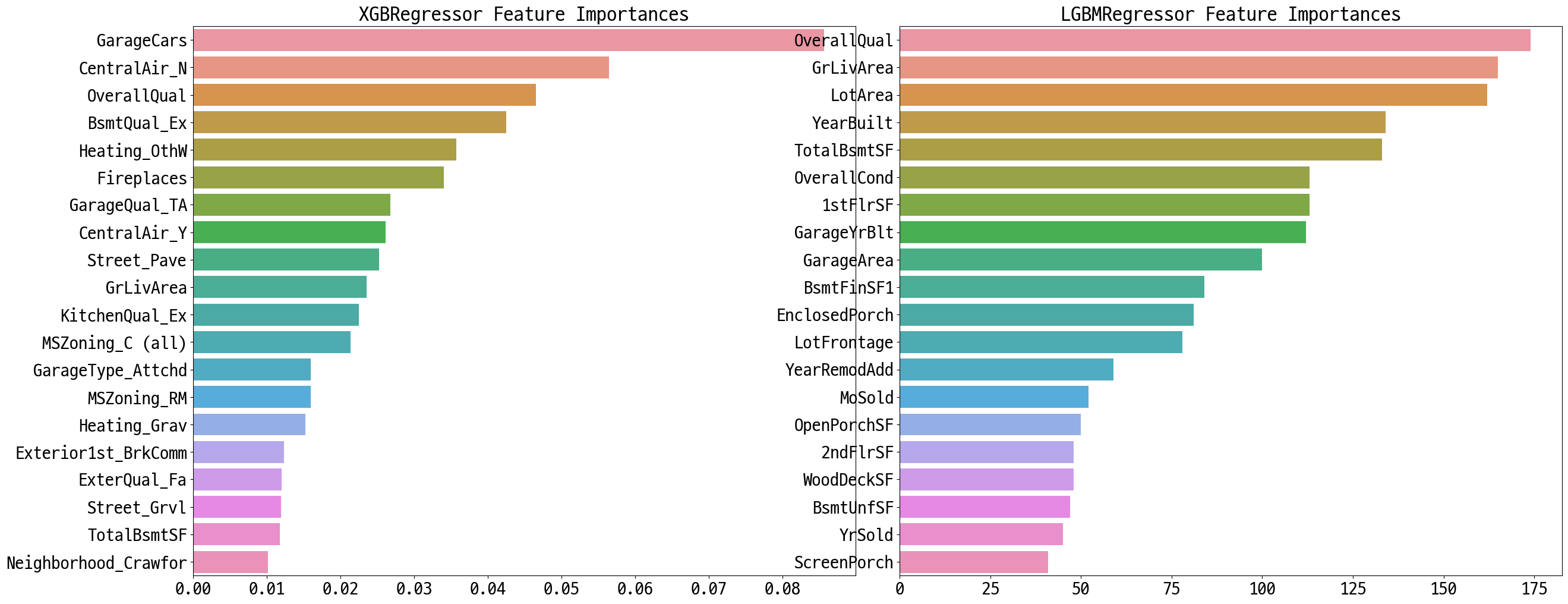
# 모델의 중요도 상위 20개의 피처명과 그때의 중요도값을 Series로 반환.
def get_top_features(model):
ftr_importances_values = model.feature_importances_
ftr_importances = pd.Series(ftr_importances_values, index=X.columns )
ftr_top20 = ftr_importances.sort_values(ascending=False)[:20]
return ftr_top20
def visualize_ftr_importances(models):
# 2개 회귀 모델의 시각화를 위해 2개의 컬럼을 가지는 subplot 생성
fig, axs = plt.subplots(figsize=(24,10),nrows=1, ncols=2)
fig.tight_layout()
# 입력인자로 받은 list객체인 models에서 차례로 model을 추출하여 피처 중요도 시각화.
for idx, model in enumerate(models):
# 중요도 상위 20개의 피처명과 그때의 중요도값 추출
ftr_top20 = get_top_features(model)
axs[idx].set_title(model.__class__.__name__+' Feature Importances', size=25)
#font 크기 조정.
for label in (axs[idx].get_xticklabels() + axs[idx].get_yticklabels()):
label.set_fontsize(22)
sns.barplot(x=ftr_top20.values, y=ftr_top20.index , ax=axs[idx])
# 앞 예제에서 print_best_params()가 반환한 GridSearchCV로 최적화된 모델의 피처 중요도 시각화
models = [best_xgb, best_lgbm]
visualize_ftr_importances(models)
회귀 모델들의 예측 결과 혼합을 통한 최종 예측
def get_rmse_pred(preds):
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
for key in preds.keys():
pred_value = preds[key]
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test , pred_value)
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
print(f'{key} 모델의 RMSE: {rmse}')
# 개별 모델의 학습
ridge_reg = Ridge(alpha=8)
ridge_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
lasso_reg = Lasso(alpha=0.001)
lasso_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 개별 모델 예측
ridge_pred = ridge_reg.predict(X_test)
lasso_pred = lasso_reg.predict(X_test)
# 개별 모델 예측값 혼합으로 최종 예측값 도출
pred = 0.4 * ridge_pred + 0.6 * lasso_pred
preds = {'최종 혼합': pred,
'Ridge': ridge_pred,
'Lasso': lasso_pred}
#최종 혼합 모델, 개별모델의 RMSE 값 출력
get_rmse_pred(preds)
최종 혼합 모델의 RMSE: 0.10007930884470506
Ridge 모델의 RMSE: 0.10345177546603253
Lasso 모델의 RMSE: 0.10024170460890033
xgb_reg = XGBRegressor(n_estimators=1000, learning_rate=0.05,
colsample_bytree=0.5, subsample=0.8)
lgbm_reg = LGBMRegressor(n_estimators=1000, learning_rate=0.05, num_leaves=4,
subsample=0.6, colsample_bytree=0.4, reg_lambda=10, n_jobs=-1)
xgb_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
lgbm_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
xgb_pred = xgb_reg.predict(X_test)
lgbm_pred = lgbm_reg.predict(X_test)
pred = 0.5 * xgb_pred + 0.5 * lgbm_pred
preds = {'최종 혼합': pred,
'XGBM': xgb_pred,
'LGBM': lgbm_pred}
get_rmse_pred(preds)
최종 혼합 모델의 RMSE: 0.10170077353447762
XGBM 모델의 RMSE: 0.10738295638346222
LGBM 모델의 RMSE: 0.10382510019327311
Reference
- 이 포스트는 SeSAC 인공지능 자연어처리, 컴퓨터비전 기술을 활용한 응용 SW 개발자 양성 과정 - 심선조 강사님의 강의를 정리한 내용입니다.

댓글남기기