자연어 처리 - RNN의 기초
순환 신경망
RNN 내부의 이해
- RNN(Recurrent Neural Network)
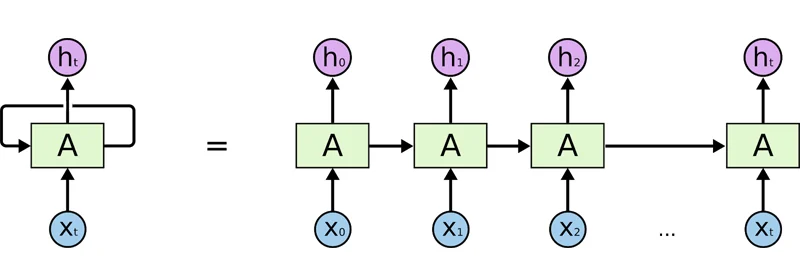
현재 대상은 과거 대상 출력의 중첩.. 다시(re) 현재(current) => Dense 학습 => 미래 예측
현재입력의 가중치 + 과거출력의 가중치 = 현재출력
미래입력의 가중치 + 현재출력의 가중치 = 미래예측

하나 입력 -> 여러 출력 (단어 하나에 대한 설명 출력, 단어 하나에 대한 시, 가사 출력)
여러 입력 -> 하나 출력 (리뷰 분석)
여러 입력 -> 여러 출력 (번역, 채팅)
파이썬 코드로 RNN 구현
현재output = 현재input + 과거output
\[h_t = tanh(W_x*X_t + W_h*h_{t-1} + bias)\]# Xt: 가상 입력 데이터(random)
import numpy as np
timesteps = 10 # vocab_size: 10 # 시점의 수, 자연어에서 문장의 단어 길이
input_dim = 4 # vector_size: 4 # 입력 차원, 자연어에서 단어당 벡터 차원(임베딩 크기)
inputs = np.random.random((timesteps, input_dim)) # (가사 분석 예제: vocab_size=20, vector_size=10)
inputs
array([[0.74753102, 0.62893607, 0.05745559, 0.38066882],
[0.58506307, 0.87763485, 0.91162332, 0.0628778 ],
[0.68316771, 0.88058488, 0.78144498, 0.75100929],
[0.10312951, 0.65993162, 0.44587026, 0.91094498],
[0.2528351 , 0.88598728, 0.23559254, 0.6235126 ],
[0.64041994, 0.36931837, 0.51040967, 0.77199075],
[0.22431365, 0.5697359 , 0.18045728, 0.35358678],
[0.49192818, 0.99818081, 0.54726083, 0.14552422],
[0.35977994, 0.55528925, 0.96489929, 0.73200054],
[0.92577408, 0.43182119, 0.31244799, 0.01688936]])
hidden_units = 8 # 은닉 상태 크기 , RNN 메모리 셀의 용량
hidden_state = np.zeros((hidden_units,)) # 초기 은닉 상태(0)
hidden_state
array([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
Wx = np.random.random((hidden_units, input_dim)) # 현재 입력의 가중치
Wh = np.random.random((hidden_units, hidden_units)) # 과거 출력의 가중치
b = np.random.random((hidden_units, )) # bias의 크기
Wx.shape, Wh.shape, b.shape
((8, 4), (8, 8), (8,))
\(W_x(8,4)*X_t(4,1) + W_h(8,8)*h_{t-1}(8,1) + b(8,1)\)
= (8,1) + (8,1) + (8,1) = (8,1)
hidden_state_list = []
# 각 시점 별 입력값
for input_one in inputs: # 10번의 반복(10단어)
# ht = tanh(Wx*Xt+Wh*h(t-1)+bias
# 현재출력 = tanh(Wx*입력 + Wh*과거출력 + 절편)
ht_res = np.tanh(np.dot(Wx, input_one) + np.dot(Wh, hidden_state) + b)
hidden_state_list.append([ht_res])
hidden_state = ht_res
hidden_state_list
[[array([0.88978338, 0.8879699 , 0.85668103, 0.97751828, 0.88561886,
0.79589261, 0.90716733, 0.89132151])],
[array([0.99992805, 0.99973896, 0.99992999, 0.99995474, 0.99999273,
0.99993177, 0.99995264, 0.99999852])],
[array([0.99999118, 0.99997027, 0.99997646, 0.999987 , 0.99999768,
0.99998782, 0.9999938 , 0.9999996 ])],
[array([0.99996839, 0.99993103, 0.99994563, 0.99992591, 0.99999409,
0.99997695, 0.99999088, 0.99999929])],
[array([0.99997157, 0.99992539, 0.99995138, 0.99993123, 0.99999308,
0.99997287, 0.99998556, 0.99999951])],
[array([0.99997933, 0.99994226, 0.99996991, 0.99994518, 0.99999614,
0.99997885, 0.99999056, 0.99999885])],
[array([0.99993052, 0.99981093, 0.99994585, 0.99981806, 0.99999162,
0.9999543 , 0.99997407, 0.99999907])],
[array([0.99997243, 0.99989107, 0.99996807, 0.99996434, 0.99999616,
0.99997352, 0.99998058, 0.99999964])],
[array([0.99997574, 0.99992922, 0.99996699, 0.99996917, 0.99999753,
0.99998319, 0.99999292, 0.99999926])],
[array([0.99996494, 0.99985048, 0.99997639, 0.99991676, 0.99999566,
0.99996135, 0.99997014, 0.99999891])]]
Keras로 RNN 구현
from keras.layers import SimpleRNN
SimpleRNN(32) # hidden_units(은닉층), Conv2D(64;필터갯수), Dense(10)
SimpleRNN(32, input_shape=(timesteps, input_dim))
SimpleRNN(32, input_length=timesteps, input_dim=input_dim) # input_shape의 다른 표현
SimpleRNN(32, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(timesteps, input_dim)) # return_sequences=False가 기본값
SimpleRNN(32, return_sequences=True, return_state=True, input_shape=(timesteps, input_dim)) # return_state=False가 기본값
<keras.layers.rnn.simple_rnn.SimpleRNN at 0x18ca89c3370>
파라미터
from keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3, input_shape=(10, 4)) # SimpleRNN(은닉 상태 크기, input_shape=(길이, 임베딩벡터 차원수))
])
model.summary()
# Wx:3*4, Wh:3*3, b:3 => 파라미터 수: 12+9+3=24
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
simple_rnn_5 (SimpleRNN) (None, 3) 24
=================================================================
Total params: 24
Trainable params: 24
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
model = Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3, batch_input_shape=(5, 10, 4))
]) # batch_size 포함
model.summary()
Model: "sequential_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
simple_rnn_6 (SimpleRNN) (5, 3) 24
=================================================================
Total params: 24
Trainable params: 24
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
model = Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3, input_shape=(10, 4), return_sequences=True)
]) # (10개의 상태)*4 -> (10개의 상태)*3 (모든 시간대의 상태들을 출력)
model.summary()
Model: "sequential_2"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
simple_rnn_7 (SimpleRNN) (None, 10, 3) 24
=================================================================
Total params: 24
Trainable params: 24
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
# Deep RNN(심층 RNN)
model = Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3, input_shape=(10, 4), return_sequences=True), # 모든 시간대의 상태를 모두 다음 RNN에 넣는다.
SimpleRNN(3, return_sequences=True) # 분류의 문제로 하나의 output이 필요할 경우 False # 번역과 같이 여러 출력이 필요할 경우는 True
])
model.summary()
Model: "sequential_3"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
simple_rnn_8 (SimpleRNN) (None, 10, 3) 24
simple_rnn_9 (SimpleRNN) (None, 10, 3) 21
=================================================================
Total params: 45
Trainable params: 45
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
return_state
X_train = np.random.random((4, 5))
X_train
array([[0.84867266, 0.92500879, 0.48712611, 0.71488416, 0.19518211],
[0.73918089, 0.85186399, 0.84740328, 0.02133248, 0.38764084],
[0.13385885, 0.54036416, 0.57698601, 0.97540603, 0.28678388],
[0.68139167, 0.33052752, 0.11929124, 0.74840668, 0.79541883]])
X_train = X_train.reshape(-1, 4, 5)
X_train
array([[[0.84867266, 0.92500879, 0.48712611, 0.71488416, 0.19518211],
[0.73918089, 0.85186399, 0.84740328, 0.02133248, 0.38764084],
[0.13385885, 0.54036416, 0.57698601, 0.97540603, 0.28678388],
[0.68139167, 0.33052752, 0.11929124, 0.74840668, 0.79541883]]])
X_train.shape
(1, 4, 5)
rnn = SimpleRNN(3)
hidden_state = rnn(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state
(TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[-0.40793645, -0.2913194 , -0.24908637]], dtype=float32)>)
- return_sequences=True
rnn = SimpleRNN(3, return_sequences=True)
hidden_state = rnn(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state
(TensorShape([1, 4, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 4, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[[-0.9403634 , -0.03043845, -0.45691478],
[-0.94018376, 0.76025677, 0.3420539 ],
[-0.9167551 , 0.8216615 , -0.7125676 ],
[-0.9674791 , 0.65315086, -0.3347327 ]]], dtype=float32)>)
- return_sequences=True, return_state=True
rnn = SimpleRNN(3, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
hidden_state, last_state = rnn(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state, last_state.shape, last_state
# hidden_state중에서 마지막 state 출력
(TensorShape([1, 4, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 4, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[[-0.06870986, 0.21422698, 0.83428085],
[ 0.35201848, 0.4577477 , 0.86182594],
[-0.17319617, 0.9280718 , 0.11305412],
[ 0.12878269, 0.24987462, 0.3398647 ]]], dtype=float32)>,
TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[0.12878269, 0.24987462, 0.3398647 ]], dtype=float32)>)
- return_state=True
rnn = SimpleRNN(3, return_state=True)
hidden_state, last_state = rnn(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state, last_state.shape, last_state
(TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[-0.698511 , -0.7901636, 0.860371 ]], dtype=float32)>,
TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[-0.698511 , -0.7901636, 0.860371 ]], dtype=float32)>)
양방향 순환 신경망
Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network
from keras.layers import Bidirectional
model = Sequential([
Bidirectional(SimpleRNN(3, return_sequences=True), input_shape=(10, 4))
])
model.summary()
# 3*3 + 3*4 + 3 = 24 => 양방향 24*2 = 48
# 나는 오늘 [ 치킨 / 자전거 / 집 ] 먹고 싶다
# 문맥상 다른방향에서의(뒤의 '먹고 싶다'로) 유추가 필요한 경우 양방향RNN이 필요하다.
Model: "sequential_4"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
bidirectional (Bidirectiona (None, 10, 6) 48
l)
=================================================================
Total params: 48
Trainable params: 48
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
LSTM
Long Short Term Memory

RNN은 라인(시간, 흐름)이 길어질수록 과거의 입력값이 미치는 영향이 희석된다!
과거의 값을 일부는 그대로(Cell state), 일부는 현재와 혼합해 과거의 값이 미치는 영향을 보존해 RNN을 보강 => LSTM
LSTM(Long Short Term Memory) - RNN을 사용할 때 라인이 길어 과거의 영향이 줄어들 경우 사용한다.
LSTM은 연산과정이 오래 걸리므로 Long Term이 필요없을 경우 RNN만 사용하여도 충분하다.
LSTM은 cell state를 신경써야한다.
from keras.layers import LSTM
- return_sequences=False, return_state=True
lstm = LSTM(3, return_sequences=False, return_state=True)
hidden_state, last_state, last_cell_state = lstm(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state, last_state.shape, last_state, last_cell_state.shape, last_cell_state
(TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[-0.38975152, 0.2563774 , -0.17216882]], dtype=float32)>,
TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[-0.38975152, 0.2563774 , -0.17216882]], dtype=float32)>,
TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[-0.9090795 , 0.5851274 , -0.31715822]], dtype=float32)>)
- return_sequences=True, return_state=True
lstm = LSTM(3, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
hidden_state, last_state, last_cell_state = lstm(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state, last_state.shape, last_state, last_cell_state.shape, last_cell_state
(TensorShape([1, 4, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 4, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[[ 0.04533345, 0.06418427, 0.05147654],
[-0.08249751, 0.0670073 , 0.07319792],
[-0.0207686 , 0.10505619, 0.15805441],
[ 0.10491455, 0.20994772, 0.04596758]]], dtype=float32)>,
TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[0.10491455, 0.20994772, 0.04596758]], dtype=float32)>,
TensorShape([1, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[0.1839388 , 0.44923508, 0.06741269]], dtype=float32)>)
- return_sequences=True, return_state=False
lstm = LSTM(3, return_sequences=True, return_state=False)
hidden_state = lstm(X_train)
hidden_state.shape, hidden_state
(TensorShape([1, 4, 3]),
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 4, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[[-0.02282599, 0.26034266, -0.22408676],
[-0.00944753, 0.33086398, -0.35179478],
[-0.07629474, 0.4781887 , -0.3323913 ],
[-0.1748439 , 0.511292 , -0.44997412]]], dtype=float32)>)
Reference
- TELUS International: What’s the difference between CNN and RNN?
- ratsgo: RNN과 LSTM을 이해해보자!
- wikidocs: 한땀한땀 딥러닝 컴퓨터 비전 백과사전


댓글남기기