자연어 처리 - Seq2seq와 챗봇 만들기
Seq2seq 모델
-
Sequence to Sequence: 하나의 텍스트 문장이 들어가면 하나의 텍스트 문장을 출력한다.
기계 번역, 텍스트 요약, 이미지 설명, 대화 모델 등 다양한 분야에서 활용되고 있다. -
구조
크게 인코더(Encoder)부분과 디코더(Decoder)부분으로 나뉜다.
인코더 부분에서 입력값을 받아 입력값의 정보를 담은 벡터를 만들어낸다.
이후 디코더에서 이 벡터를 활용해 재귀적으로 출력값을 만들어내는 구조다.
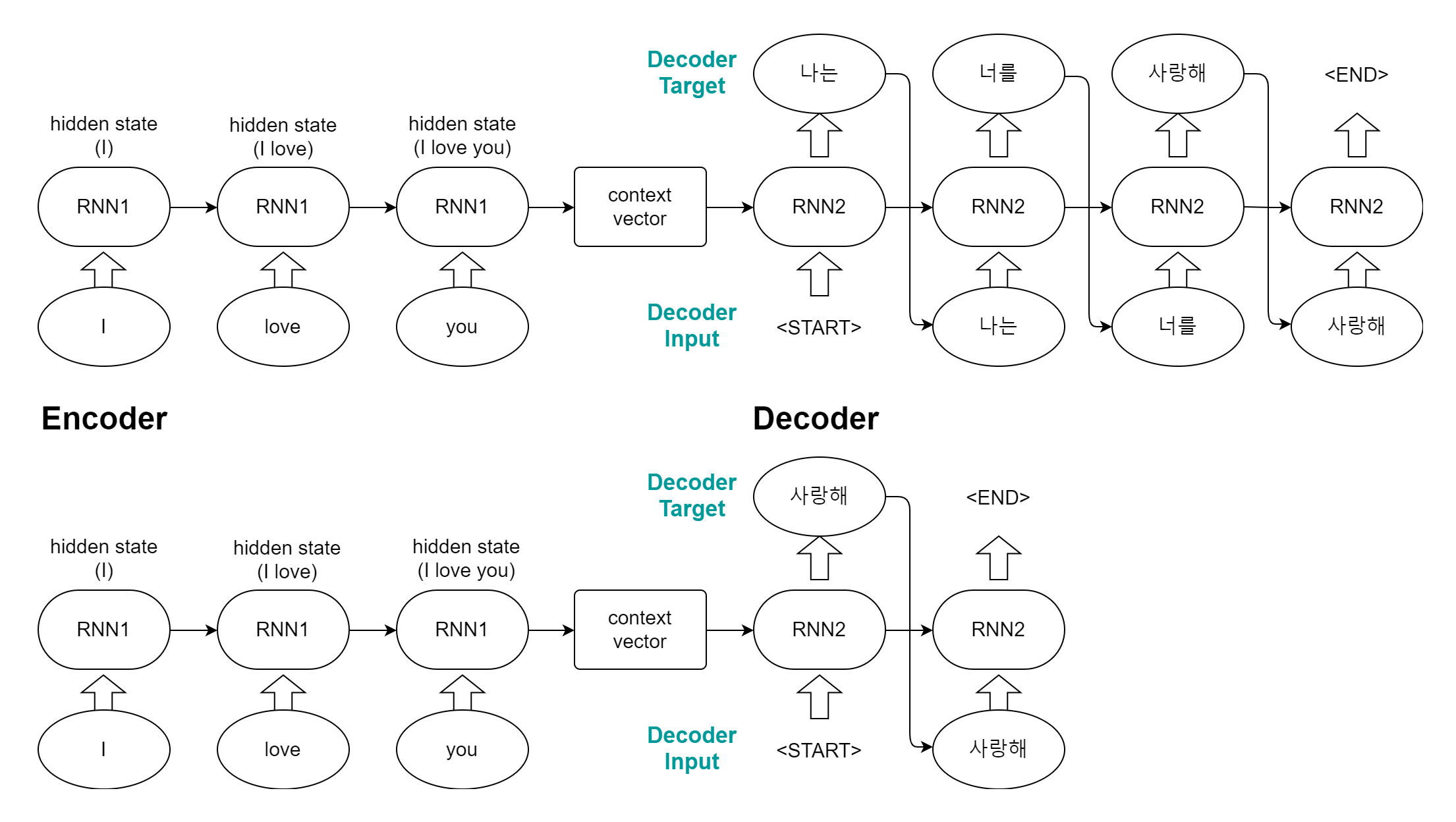
인코더에서 RNN을 거쳐 마지막에 생성된 hidden state를 문맥(context vector)으로 디코더에 전달된다.
- 어텐션 (attention)
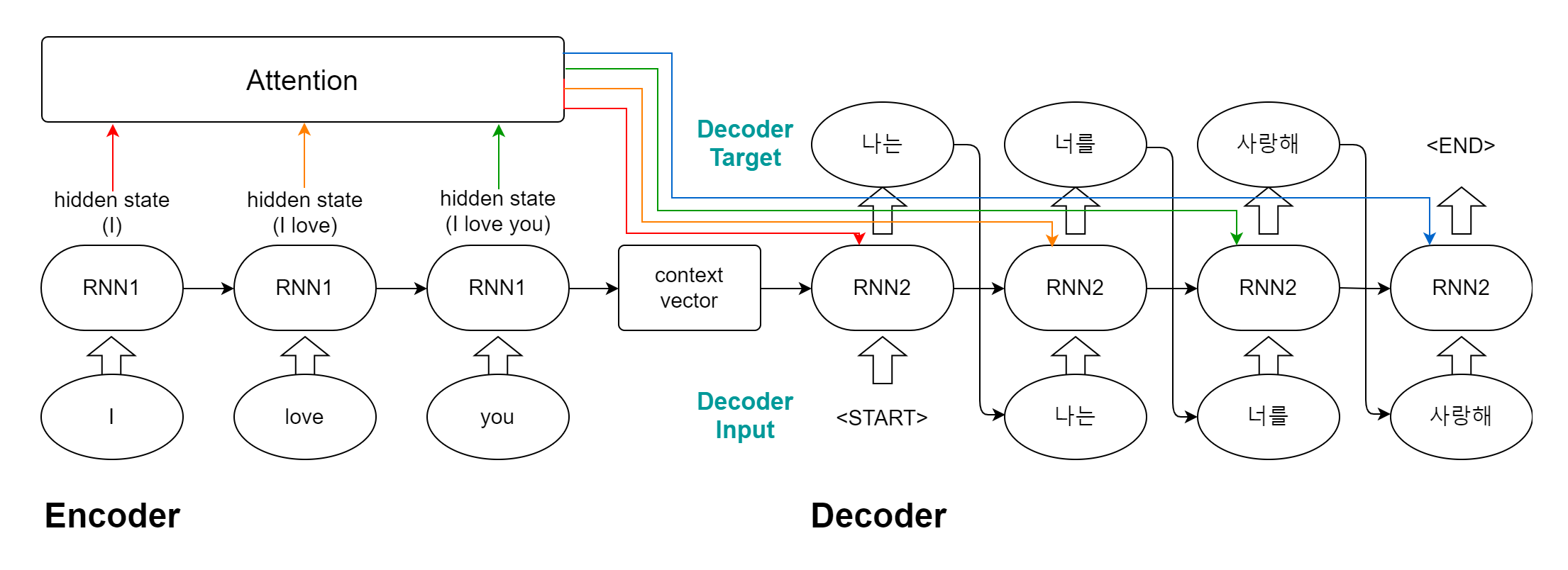
기존 seq2seq 모델은 문장이 길어질수록 더 많은 정보를 고정된 길이에 담야야 하므로 정보의 손실이 발생할 수 있었다.
이를 해결하기 위한 방법으로 어텐션이 추가되었다.
인코더에서 hidden state의 값을 통해 어텐션을 계산하고 디코더의 각 sequence마다 계산된 어텐션을 추가로 입력한다.
어텐션도 함께 학습을 진행하게 되며 학습을 통해 디코더의 각 sequence마다 어텐션의 가중치를 다르게 적용하는 식이다.
챗봇 만들기 - seq2seq
preprocess.py
데이터 불러오기, 다양한 기능의 함수 구현
import os, re, json
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from tqdm import tqdm
from konlpy.tag import Okt
FILTERS = "([~.,!?\"':;)(])"
# 토큰 지정
PAD = "<PAD>"
STD = "<SOS>" # start of sentence
END = "<END>"
UNK = "<UNK>" # Unknown, OOV(Out of Vocabulary)
# 토큰에 idx부여(예약어)
PAD_INDEX = 0
STD_INDEX = 1
END_INDEX = 2
UNK_INDEX = 3
MARKER = [PAD, STD, END, UNK]
# 미리 컴파일 해서 패턴을 사용할 때 컴파일 하는 시간 단축
CHANGE_FILTER = re.compile(FILTERS)
MAX_SEQUENCE = 25
데이터 불러오기
모든 데이터를 학습시키면 epoch당 2시간이 필요하여 임의로 앞의 111개만 테스트로 작업했다.
# 데이터 불러오기
def load_data(path):
data_df = pd.read_csv(path, header=0)
data_df = data_df[:111] # ..시간단축을 위해..
question, answer = list(data_df['Q']), list(data_df['A'])
return question, answer
# 문장의 특수기호 제거, 띄어쓰기 기준으로 단어 나누기
def data_tokenizer(data):
words = []
for sent in data:
# 필터로 대체(특수기호들을 ""로 변환->삭제)
sent = re.sub(CHANGE_FILTER, "", sent)
for word in sent.split():
words.append(word)
return [word for word in words if word]
# Okt 형태소 분석하여 공백으로 구분한 뒤 문자열로 저장
def prepro_like_morphlized(data):
morph_analyzer = Okt()
result_data = list()
for seq in tqdm(data):
morphlized_seq = " ".join(morph_analyzer.morphs(seq.replace(' ', '')))
result_data.append(morphlized_seq)
return result_data
단어사전 만들기
# 단어사전 만들기
def load_vocabulary(path, vocab_path, tokenize_as_morph=False):
vocab_list = []
# 단어사전 존재 확인
if not os.path.exists(vocab_path):
if os.path.exists(path):
data_df = pd.read_csv(path, encoding='utf-8')
question, answer = list(data_df['Q']), list(data_df['A'])
if tokenize_as_morph:
question = prepro_like_morphlized(question)
answer = prepro_like_morphlized(answer)
data = []
data.extend(question)
data.extend(answer)
words = data_tokenizer(data)
words = list(set(words)) # 중복 제거
words[:0] = MARKER # 마커를 맨 앞에 삽입
# 작업물 기록
with open(vocab_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as vf:
for word in words:
vf.write(word + '\n')
with open(vocab_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as vf:
for line in vf:
vocab_list.append(line.strip()) # 줄바꿈 제거
word2idx, idx2word = make_vocabulary(vocab_list)
return word2idx, idx2word, len(word2idx)
def make_vocabulary(vocab_list):
# {단어:idx}
word2idx = {word:idx for idx, word in enumerate(vocab_list)}
# {idx:단어}
idx2word = {idx:word for idx, word in enumerate(vocab_list)}
return word2idx, idx2word
주의할 점은 {단어:idx}의 idx는 정수형태로 저장되지만 {idx:단어}의 idx는 key값이므로 문자열형태로 저장된다.
전처리
# 단어 사전으로 인코더 전처리
def enc_processing(value, dictionary, tokenize_as_morph=False):
sequences_input_idx = []
sequences_length = []
if tokenize_as_morph:
value = prepro_like_morphlized(value)
for sequence in value: # 문장 단위 분해
sequence = re.sub(CHANGE_FILTER, "", sequence) # 특수기호 제거
sequence_idx = []
for word in sequence.split(): # 단어 단위 분해
if dictionary.get(word) is not None:
sequence_idx.extend([dictionary[word]])
else:
sequence_idx.extend([dictionary[UNK]])
# 문장 길이 조절
if len(sequence_idx) > MAX_SEQUENCE:
sequence_idx = sequence_idx[:MAX_SEQUENCE]
sequences_length.append(len(sequence_idx))
sequence_idx += (MAX_SEQUENCE - len(sequence_idx)) * [dictionary[PAD]] # 빈칸 padding
sequences_input_idx.append(sequence_idx)
return np.asarray(sequences_input_idx), sequences_length # asarray: array(copy=False), 원본이 변경되면 array도 변경됨
# 디코더 입력 전처리
def dec_input_processing(value, dictionary, tokenize_as_morph=False):
sequences_input_idx = []
sequences_length = []
if tokenize_as_morph:
value=prepro_like_morphlized(value)
for sequence in value:
sequence = re.sub(CHANGE_FILTER, "", sequence)
# sequence_idx = []
sequence_idx = [dictionary[STD]] + [dictionary[word] if word in dictionary else dictionary[UNK] for word in sequence.split()]
if len(sequence_idx) > MAX_SEQUENCE:
sequence_idx = sequence_idx[:MAX_SEQUENCE]
sequences_length.append(len(sequence_idx))
sequence_idx += (MAX_SEQUENCE - len(sequence_idx)) * [dictionary[PAD]]
sequences_input_idx.append(sequence_idx)
return np.asarray(sequences_input_idx), sequences_length
# 디코더 타겟 전처리
def dec_target_processing(value, dictionary, tokenize_as_morph=False):
sequences_target_idx = []
if tokenize_as_morph:
value = prepro_like_morphlized(value)
for sequence in value:
sequence = re.sub(CHANGE_FILTER, "", sequence)
sequence_idx = [dictionary[word] if word in dictionary else dictionary[UNK] for word in sequence.split()]
if len(sequence_idx) >= MAX_SEQUENCE:
sequence_idx = sequence_idx[:MAX_SEQUENCE-1] + [dictionary[END]]
else:
sequence_idx += [dictionary[END]]
sequence_idx += (MAX_SEQUENCE - len(sequence_idx)) * [dictionary[PAD]]
sequences_target_idx.append(sequence_idx)
return np.asarray(sequences_target_idx)
Preprocess.ipynb
preprocess.py의 함수를 불러와 학습 데이터 준비
# from preprocess import *
PATH = 'datasets/data_in/ChatBotData.csv'
VOCAB_PATH = 'datasets/data_in/vocabulary.txt'
# 데이터 불러오기
inputs, outputs = load_data(PATH) # inputs: 인코더용(Q), outputs: 디코더용(A)
# 띄어쓰기 단위 토큰화하여 단어 사전 생성
char2idx, idx2char, vocab_size = load_vocabulary(PATH, VOCAB_PATH, tokenize_as_morph=False)
# 인코더 입력 전처리
idx_inputs, input_seq_len = enc_processing(inputs, char2idx, tokenize_as_morph=False)
# 디코더 입력 전처리
idx_outputs, output_seq_len = dec_input_processing(outputs, char2idx, tokenize_as_morph=False)
# 디코더 타겟 전처리
idx_targets = dec_target_processing(outputs, char2idx, tokenize_as_morph=False)
data_config = {'char2idx':char2idx,
'idx2char':idx2char,
'vocab_size':vocab_size,
'pad_symbol':PAD,
'std_symbol':STD,
'end_symbol':END,
'unk_symbol':UNK}
DATA_IN_PATH = 'datasets/data_in/'
TRAIN_INPUTS = 'train_inputs.npy'
TRAIN_OUTPUTS = 'train_outputs.npy'
TRAIN_TARGETS = 'train_targets.npy'
DATA_CONFIGS = 'data_configs.json'
# 인덱스 데이터와 단어사전 dictionary 객체를 np, json 형식으로 저장
np.save(open(DATA_IN_PATH + TRAIN_INPUTS, 'wb'), idx_inputs)
np.save(open(DATA_IN_PATH + TRAIN_OUTPUTS, 'wb'), idx_outputs)
np.save(open(DATA_IN_PATH + TRAIN_TARGETS, 'wb'), idx_targets)
json.dump(data_config, open(DATA_IN_PATH + DATA_CONFIGS, 'w'))
seq2seq2.ipynb
모델 구현, 학습, 추론
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# from preprocess import *
# 시각화 함수
def plot_graphs(history, string):
plt.plot(history.history[string])
plt.plot(history.history['val_'+string], '')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel(string)
plt.legend([string, 'val_'+string])
plt.show()
DATA_IN_PATH = 'datasets/data_in/'
DATA_OUT_PATH = 'datasets/data_out/'
TRAIN_INPUTS = 'train_inputs.npy'
TRAIN_OUTPUTS = 'train_outputs.npy'
TRAIN_TARGETS = 'train_targets.npy'
DATA_CONFIGS = 'data_configs.json'
SEED_NUM = 1234
tf.random.set_seed(SEED_NUM)
idx_inputs = np.load(open(DATA_IN_PATH + TRAIN_INPUTS, 'rb'))
idx_outputs = np.load(open(DATA_IN_PATH + TRAIN_OUTPUTS, 'rb'))
idx_targets = np.load(open(DATA_IN_PATH + TRAIN_TARGETS, 'rb'))
prepro_configs = json.load(open(DATA_IN_PATH + DATA_CONFIGS, 'r'))
print(len(idx_inputs), len(idx_outputs), len(idx_targets))
111 111 111
# 모델 구성 변수 정의
MODEL_NAME = 'seq2seq_kor'
BATCH_SIZE = 2
MAX_SEQUENCE = 25
EPOCH = 50
UNITS = 1024
EMBEDDING_DIM = 256
VALIDATION_SPLIT = 0.1
char2idx = prepro_configs['char2idx']
idx2char = prepro_configs['idx2char']
std_idx = prepro_configs['std_symbol']
end_idx = prepro_configs['end_symbol']
vocab_size = prepro_configs['vocab_size']
인코더 구성
# 인코더 클래스
class Encoder(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, enc_units, batch_sz):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.batch_sz = batch_sz
self.enc_units = enc_units
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(self.vocab_size, self.embedding_dim)
self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.enc_units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True, recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
def call(self, x, hidden):
x = self.embedding(x)
output, state = self.gru(x, initial_state=hidden)
return output, state
def initialize_hidden_state(self, inp):
return tf.zeros((tf.shape(inp)[0], self.enc_units))
어텐션 구성
# 어텐션 클래스
class BahdanauAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, units):
super(BahdanauAttention, self).__init__()
self.W1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units) # value 학습용
self.W2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units) # query 학습용
self.V = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1) # softmax용
def call(self, query, values):
hidden_with_time_axis = tf.expand_dims(query, 1) # 차원 축의 숫자(단어의 갯수)
score = self.V(tf.nn.tanh(self.W1(values) + self.W2(hidden_with_time_axis)))
attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(score, axis=1) # 중요하게 여길 요소를 추천(softmax)
context_vector = attention_weights * values # 원본들에 가중치를 곱함=>원본 중에 중요한 것의 영향을 크게 만듬
context_vector = tf.reduce_sum(context_vector, axis=1)
return context_vector, attention_weights
디코더 구성
# 디코더 클래스
class Decoder(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, dec_units, batch_sz):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.batch_sz = batch_sz
self.dec_units = dec_units
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(self.vocab_size, self.embedding_dim)
self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.dec_units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True, recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
self.fc = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.vocab_size)
self.attention = BahdanauAttention(self.dec_units)
def call(self, x, hidden, enc_output):
context_vector, attention_weights = self.attention(hidden, enc_output)
x = self.embedding(x)
x = tf.concat([tf.expand_dims(context_vector, 1), x], axis=-1)
output, state = self.gru(x)
output = tf.reshape(output, (-1, output.shape[2])) # 차원조절
x = self.fc(output)
return x, state, attention_weights
옵티마이저, 손실함수, 정확도함수 구성
# 옵티마이저, 손실함수, 정확도함수
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True, reduction='none')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='accuracy')
# 문장의 문맥속에 하나의 단어만 masking
def loss(real, pred):
mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(real, 0))
loss_ = loss_object(real, pred)
mask = tf.cast(mask, dtype=loss_.dtype) # 타입 통일
loss_ *= mask
return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)
def accuracy(real, pred):
mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(real, 0))
mask = tf.expand_dims(tf.cast(mask, dtype=pred.dtype), axis=-1)
pred *= mask
acc = train_accuracy(real, pred)
return tf.reduce_mean(acc)
모델 구성
class seq2seq(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, enc_units, dec_units, batch_sz, end_token_idx=2):
super(seq2seq, self).__init__()
self.end_token_idx = end_token_idx
self.encoder = Encoder(vocab_size, embedding_dim, enc_units, batch_sz)
self.decoder = Decoder(vocab_size, embedding_dim, dec_units, batch_sz)
def call(self, x):
# 인코더 작업
inp, tar = x
enc_hidden = self.encoder.initialize_hidden_state(inp)
enc_output, enc_hidden = self.encoder(inp, enc_hidden)
dec_hidden = enc_hidden
# 디코더 작업
predict_tokens = list()
for t in range(0, tar.shape[1]):
dec_input = tf.dtypes.cast(tf.expand_dims(tar[:, t], 1), tf.float32)
predictions, dec_hidden, _ = self.decoder(dec_input, dec_hidden, enc_output)
predict_tokens.append(tf.dtypes.cast(predictions, tf.float32))
return tf.stack(predict_tokens, axis=1)
# 테스트 함수(output 산출 역할)
def inference(self, x):
# 인코더 작업
inp = x
enc_hidden = self.encoder.initialize_hidden_state(inp)
enc_output, enc_hidden = self.encoder(inp, enc_hidden)
dec_hidden = enc_hidden
# 디코더 작업
dec_input = tf.expand_dims([char2idx[std_idx]], 1) # 디코더에 최초 <START> 입력
predict_tokens = []
for t in range(0, MAX_SEQUENCE):
predictions, dec_hidden, _ = self.decoder(dec_input, dec_hidden, enc_output)
predict_token = tf.argmax(predictions[0])
if predict_token == self.end_token_idx:
break
predict_tokens.append(predict_token)
dec_input = tf.dtypes.cast(tf.expand_dims([predict_token], 0), tf.float32)
return tf.stack(predict_tokens, axis=0).numpy()
model = seq2seq(vocab_size, EMBEDDING_DIM, UNITS, UNITS, BATCH_SIZE, char2idx[end_idx])
model.compile(loss=loss, optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-3), metrics=[accuracy])
모델 학습
PATH = DATA_OUT_PATH + MODEL_NAME
if not(os.path.isdir(PATH)):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(PATH))
checkpoint_path = DATA_OUT_PATH + MODEL_NAME + '/weights.h5'
cp_callback = ModelCheckpoint(
checkpoint_path, monitor='val_accuracy', verbose=1, save_best_only=True, save_weights_only=True)
earlystop_callback = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_accuracy', min_delta=0.0001, patience=10)
history = model.fit([idx_inputs, idx_outputs], idx_targets, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, epochs=30,#EPOCH,
validation_split=VALIDATION_SPLIT, callbacks=[earlystop_callback, cp_callback])
Epoch 1/30
50/50 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.4414 - accuracy: 0.8555
Epoch 1: val_accuracy improved from -inf to 0.84929, saving model to datasets/data_out/seq2seq_kor\weights.h5
50/50 [==============================] - 118s 2s/step - loss: 1.4414 - accuracy: 0.8555 - val_loss: 1.6361 - val_accuracy: 0.8493
Epoch 2/30
50/50 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.9581 - accuracy: 0.8448
Epoch 2: val_accuracy improved from 0.84929 to 0.84989, saving model to datasets/data_out/seq2seq_kor\weights.h5
50/50 [==============================] - 75s 2s/step - loss: 0.9581 - accuracy: 0.8448 - val_loss: 1.7163 - val_accuracy: 0.8499
...
Epoch 29/30
50/50 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2746 - accuracy: 0.8703
Epoch 29: val_accuracy improved from 0.86929 to 0.87086, saving model to datasets/data_out/seq2seq_kor\weights.h5
50/50 [==============================] - 76s 2s/step - loss: 0.2746 - accuracy: 0.8703 - val_loss: 2.4630 - val_accuracy: 0.8709
Epoch 30/30
50/50 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2448 - accuracy: 0.8719
Epoch 30: val_accuracy improved from 0.87086 to 0.87257, saving model to datasets/data_out/seq2seq_kor\weights.h5
50/50 [==============================] - 75s 1s/step - loss: 0.2448 - accuracy: 0.8719 - val_loss: 2.4756 - val_accuracy: 0.8726
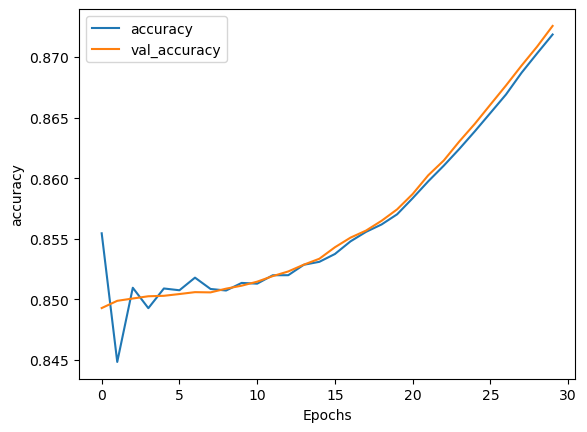
plot_graphs(history, 'accuracy')
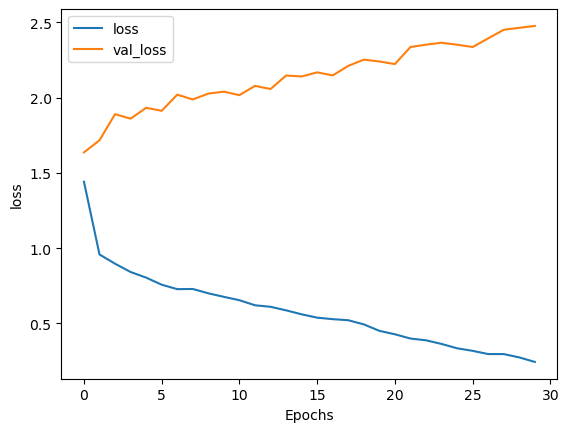
plot_graphs(history, 'loss')
SAVE_FILE_NM = 'weights.h5'
model.load_weights(os.path.join(DATA_OUT_PATH, MODEL_NAME, SAVE_FILE_NM))
query = '3박4일 놀러 가고 싶다'
test_idx_inputs, _ = enc_processing([query], char2idx)
predict_tokens = model.inference(test_idx_inputs)
print(' '.join([idx2char[str(t)] for t in predict_tokens]))
여행은 언제나 좋죠

댓글남기기