OpenCV 이미지 처리 2
13. 이미지 변형 (이진화)
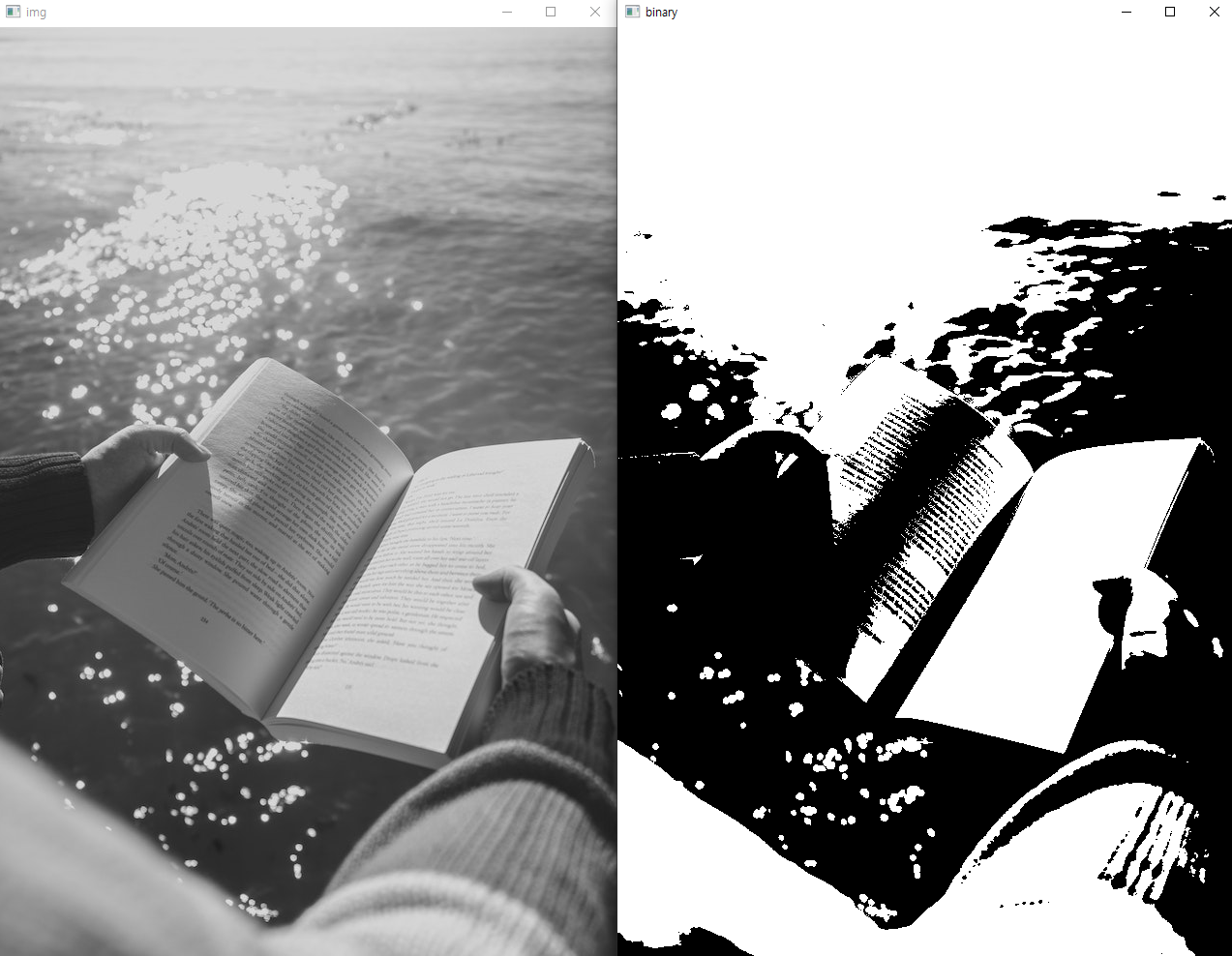
Threshold
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('book.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 127(임곗값) 기준 넘으면 255로 표현
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

Trackbar (값 변화에 따른 변형 확인)
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('book.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
def empty(pos):
# print(pos)
pass
name = 'Trackbar'
cv2.namedWindow(name)
cv2.createTrackbar('threshold', name, 127, 255, empty) # bar이름, 창이름, 초기값, 최대값, 이벤트 처리
while True:
thresh = cv2.getTrackbarPos('threshold', name) # bar이름, 창이름
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(img, thresh, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if not ret:
break
cv2.imshow(name, binary)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

그림판 제작 이미지 테스트
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('threshold.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
def empty(pos):
# print(pos)
pass
name = 'Trackbar'
cv2.namedWindow(name)
cv2.createTrackbar('threshold', name, 127, 255, empty) # bar이름, 창이름, 초기값, 최대값, 이벤트 처리
while True:
thresh = cv2.getTrackbarPos('threshold', name) # bar이름, 창이름
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(img, thresh, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
if not ret:
break
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow(name, binary)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('threshold.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
ret, binary1 = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 진한회색, 밝은회색, 흰색
ret, binary2 = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 밝은회색, 흰색
ret, binary3 = cv2.threshold(img, 195, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 흰색
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary1', binary1)
cv2.imshow('binary2', binary2)
cv2.imshow('binary3', binary3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

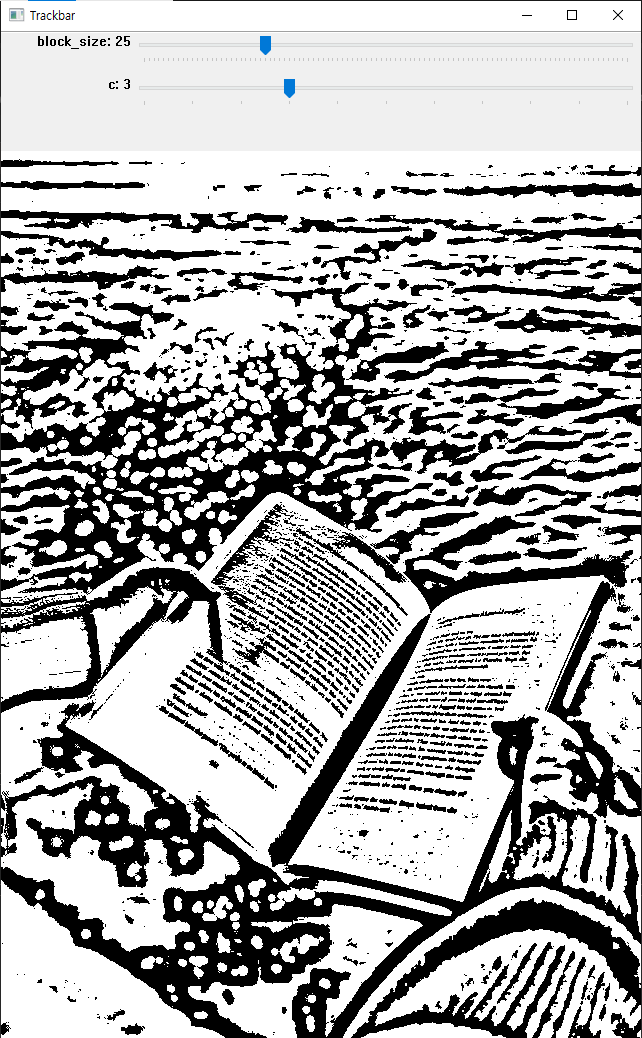
Adaptive Threshold
이미지를 작은 영역으로 나누어서 임계치 적용
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('book.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
def empty(pos):
# print(pos)
pass
name = 'Trackbar'
cv2.namedWindow(name)
cv2.createTrackbar('block_size', name, 25, 100, empty) # 홀수만 가능, 1보다는 큰 값
cv2.createTrackbar('c', name, 3, 10, empty) # 일반적으로 양수의 값을 사용
while True:
block_size = cv2.getTrackbarPos('block_size', name)
c = cv2.getTrackbarPos('c', name)
if block_size <= 1: # 1이하면 3으로
block_size = 3
if block_size % 2 == 0: # 짝수면 홀수로
block_size += 1
binary = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, block_size, c)
cv2.imshow(name, binary)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

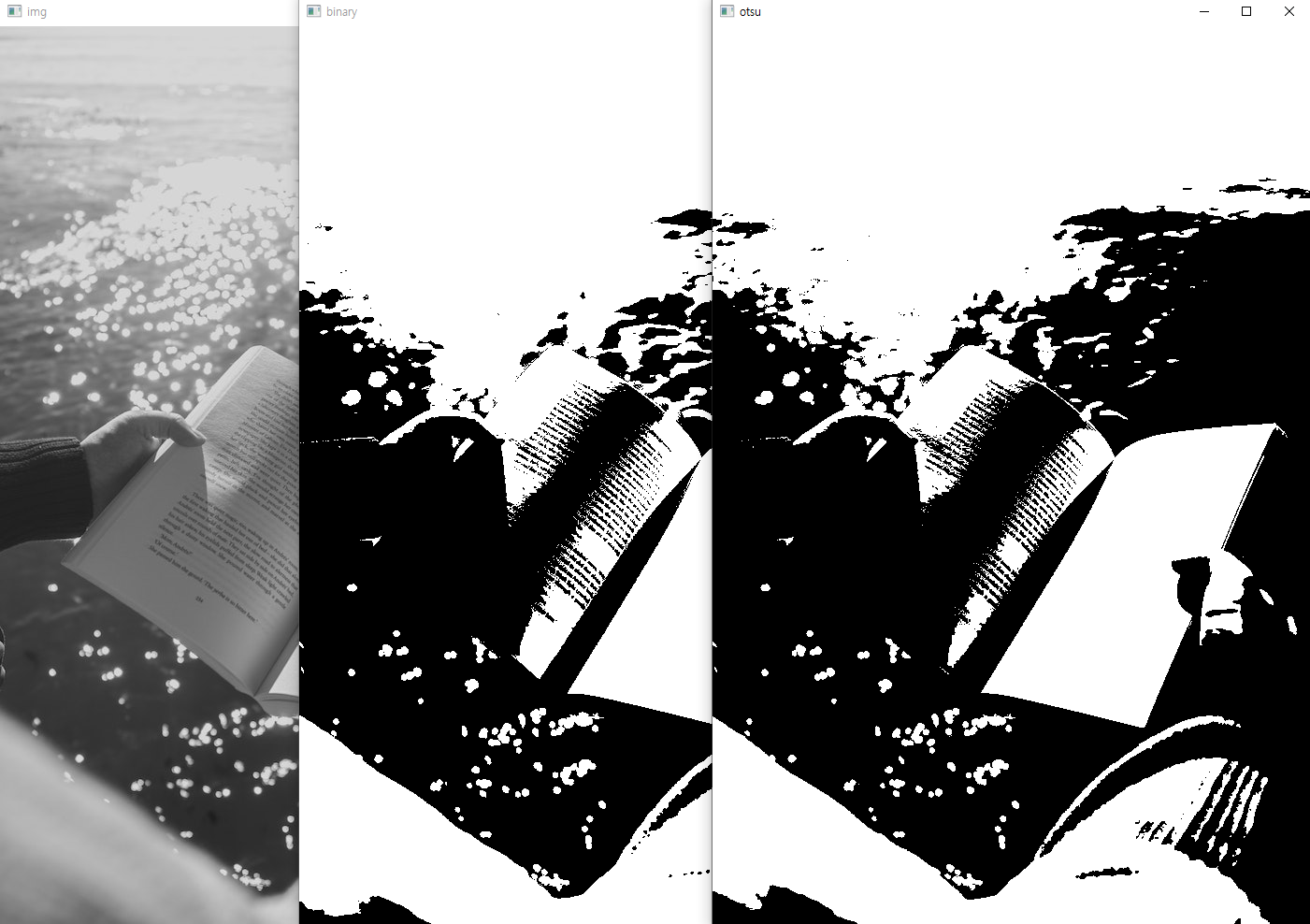
오츠 알고리즘
Bimodal Image에 사용하기 적합, 최적의 임계치를 자동으로 발견
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('book.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(img, -1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
print('otsu threshold', ret)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('binary', binary)
cv2.imshow('otsu', otsu)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
otsu threshold 138.0

14. 이미지 변환 (팽창)
이미지를 확장하여 작은 구멍을 채움
흰색 영역의 외곽 픽셀 주변에 흰색을 추가
import cv2
import numpy as np
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# kernel
img = cv2.imread('dilate.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
dilate1 = cv2.dilate(img, kernel, iterations=1) # 반복횟수
dilate2 = cv2.dilate(img, kernel, iterations=2) # 반복횟수
dilate3 = cv2.dilate(img, kernel, iterations=3) # 반복횟수
cv2.imshow('gray', img)
cv2.imshow('dilate1', dilate1)
cv2.imshow('dilate2', dilate2)
cv2.imshow('dilate3', dilate3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

15. 이미지 변환 (침식)
이미지를 깎아서 노이즈 제거
흰색 영역의 외곽 픽셀을 검은색으로 변경
import cv2
import numpy as np
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
img = cv2.imread('erode.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
erode1 = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=1) # 1회 반복
erode2 = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=2)
erode3 = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=3)
cv2.imshow('gray', img)
cv2.imshow('erode1', erode1)
cv2.imshow('erode2', erode2)
cv2.imshow('erode3', erode3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

16. 이미지 변환 (열림 & 닫힘)
열림 (Opening) : 침식 후 팽창, 깎아서 노이즈 제거 후 메움
dilate(erode(image))
import cv2
import numpy as np
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
img = cv2.imread('erode.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
erode = cv2.erode(img, kernel, iterations=3)
dilate = cv2.dilate(erode, kernel, iterations=3)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('erode', erode)
cv2.imshow('dilate', dilate)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

닫힘 (Closing) : 팽창 후 침식, 구멍을 메운 후 다시 깎음
erode(dilate(image))
import cv2
import numpy as np
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
img = cv2.imread('dilate.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
dilate = cv2.dilate(img, kernel, iterations=3)
erode = cv2.erode(dilate, kernel, iterations=3)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('dilate', dilate)
cv2.imshow('erode', erode)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

17. 이미지 검출 (경계선)
Canny Edge Detection
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('snowman.png')
canny = cv2.Canny(img, 150, 200) # 대상 이미지, minVal(하위 임곗값), maxVal(상위 임곗값)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('canny', canny)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
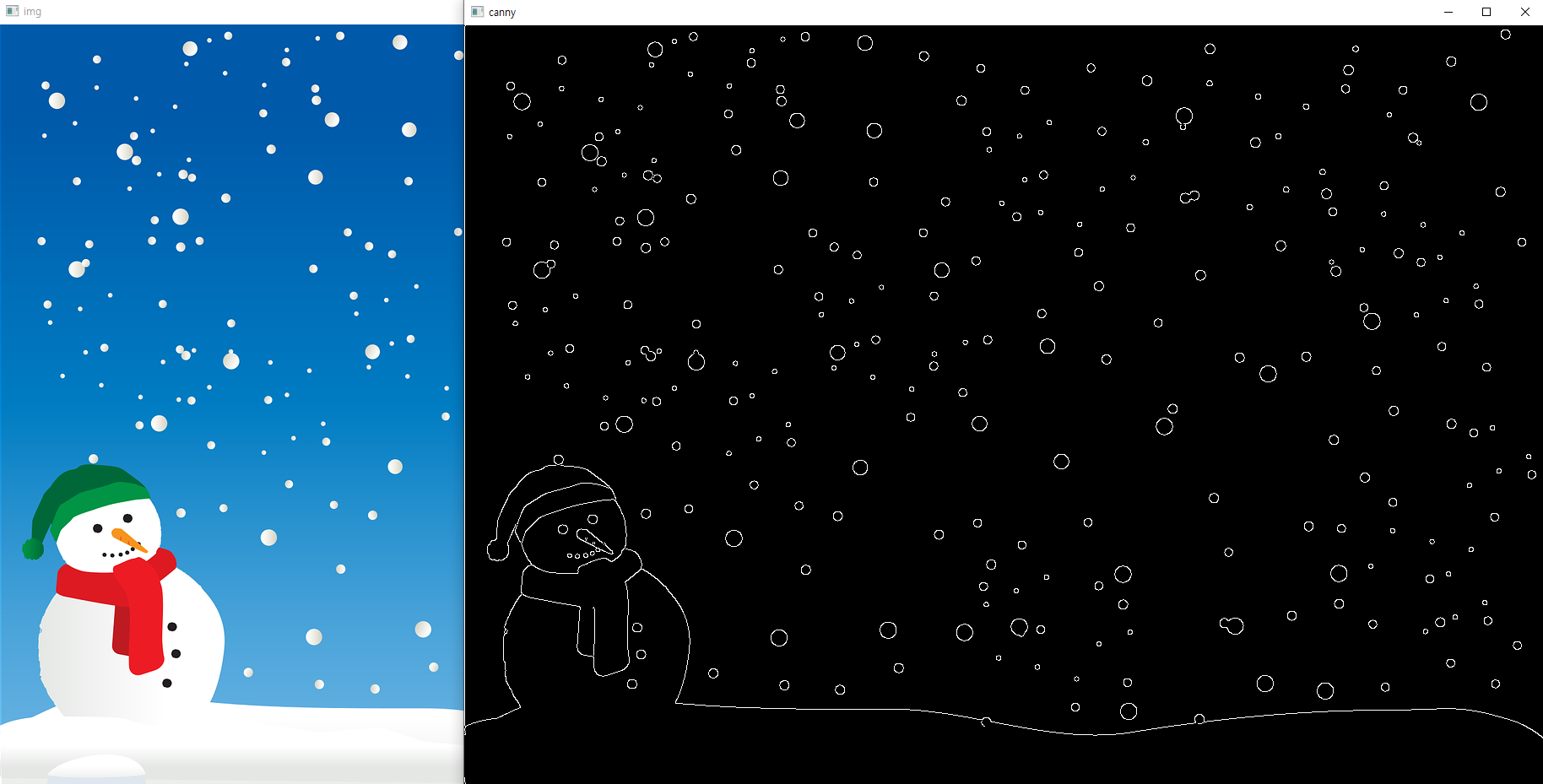

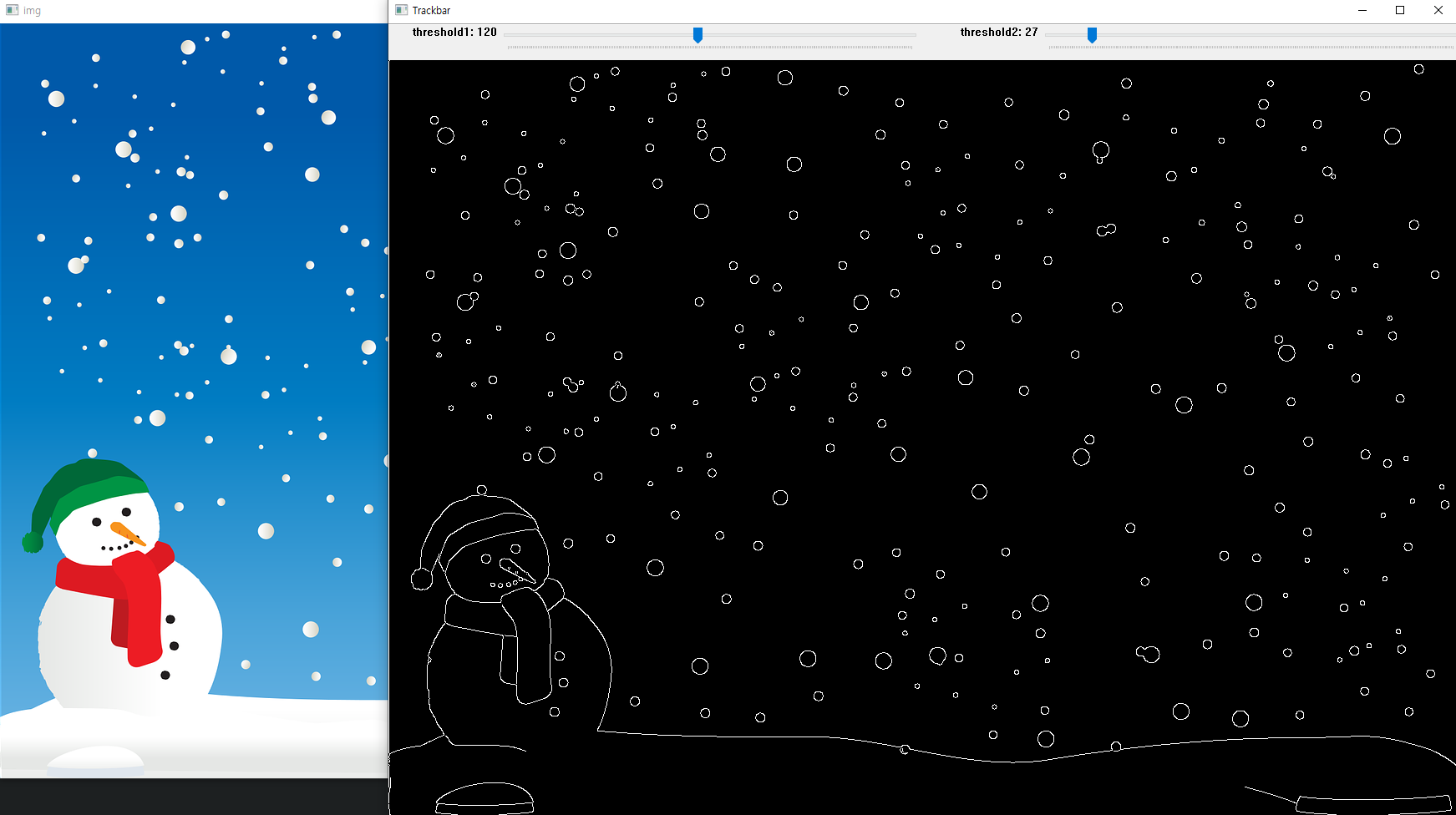
import cv2
def empty(pos):
pass
img = cv2.imread('snowman.png')
name = 'Trackbar'
cv2.namedWindow(name)
cv2.createTrackbar('threshold1', name, 0, 255, empty) # minVal
cv2.createTrackbar('threshold2', name, 0, 255, empty) # maxVal
while True:
threshold1 = cv2.getTrackbarPos('threshold1', name)
threshold2 = cv2.getTrackbarPos('threshold2', name)
canny = cv2.Canny(img, threshold1, threshold2)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow(name, canny)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
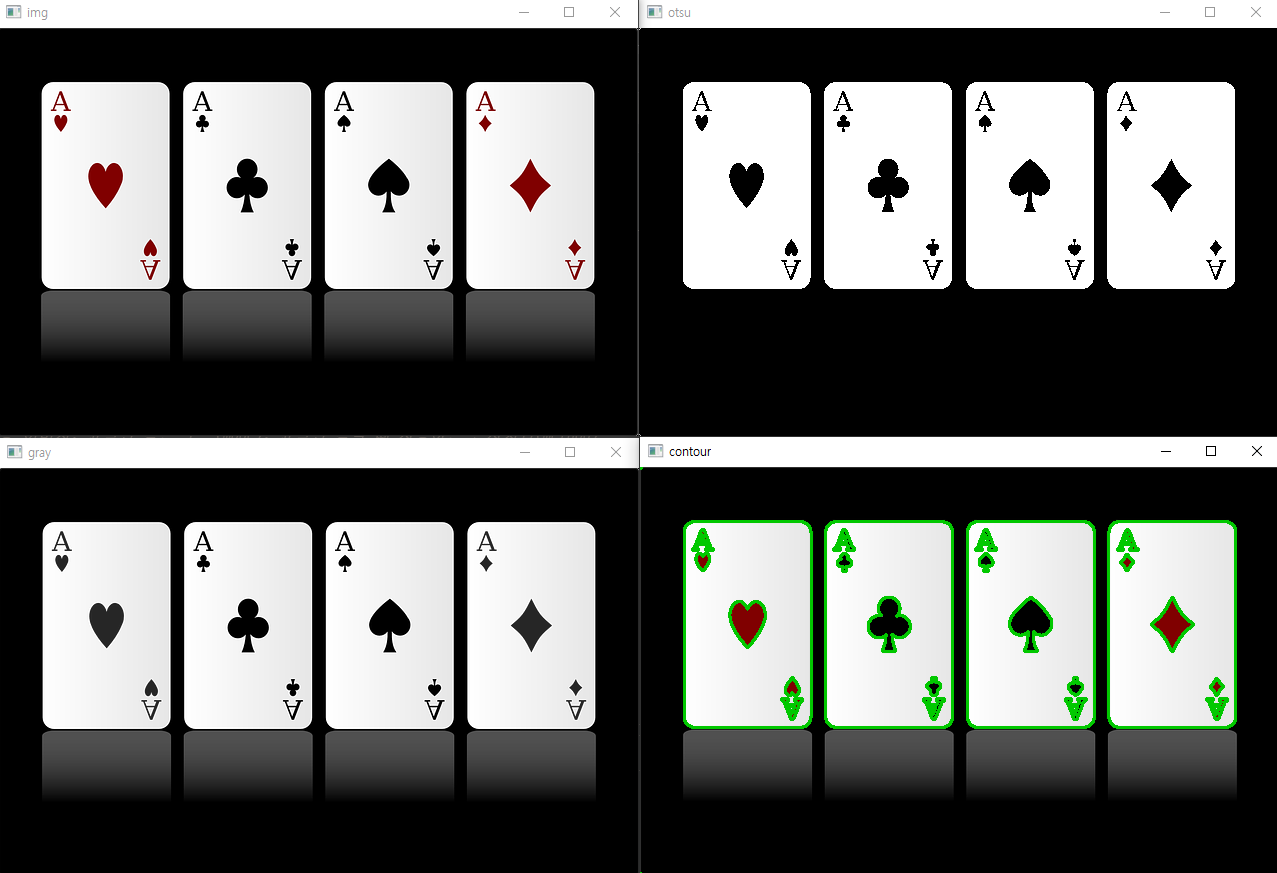
18. 이미지 검출 (윤곽선)
윤곽선 (Contour) : 경계선을 연결한 선
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
target_img = img.copy() # 사본 이미지
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(gray, -1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# 윤곽선 검출
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 윤곽선 정보, 계층 구조 = 대상 이미지, 윤곽선 찾는 모드(mode), 윤곽선 찾을 때 사용하는 근사치법(method)
# 윤곽선 그리기
COLOR = (0, 200, 2) # 녹색
cv2.drawContours(target_img, contours, -1, COLOR, 2)
# 대상 이미지, 윤곽선 정보, 인덱스(-1는 전체), 색깔, 두께
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
cv2.imshow('otsu', otsu)
cv2.imshow('contour', target_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
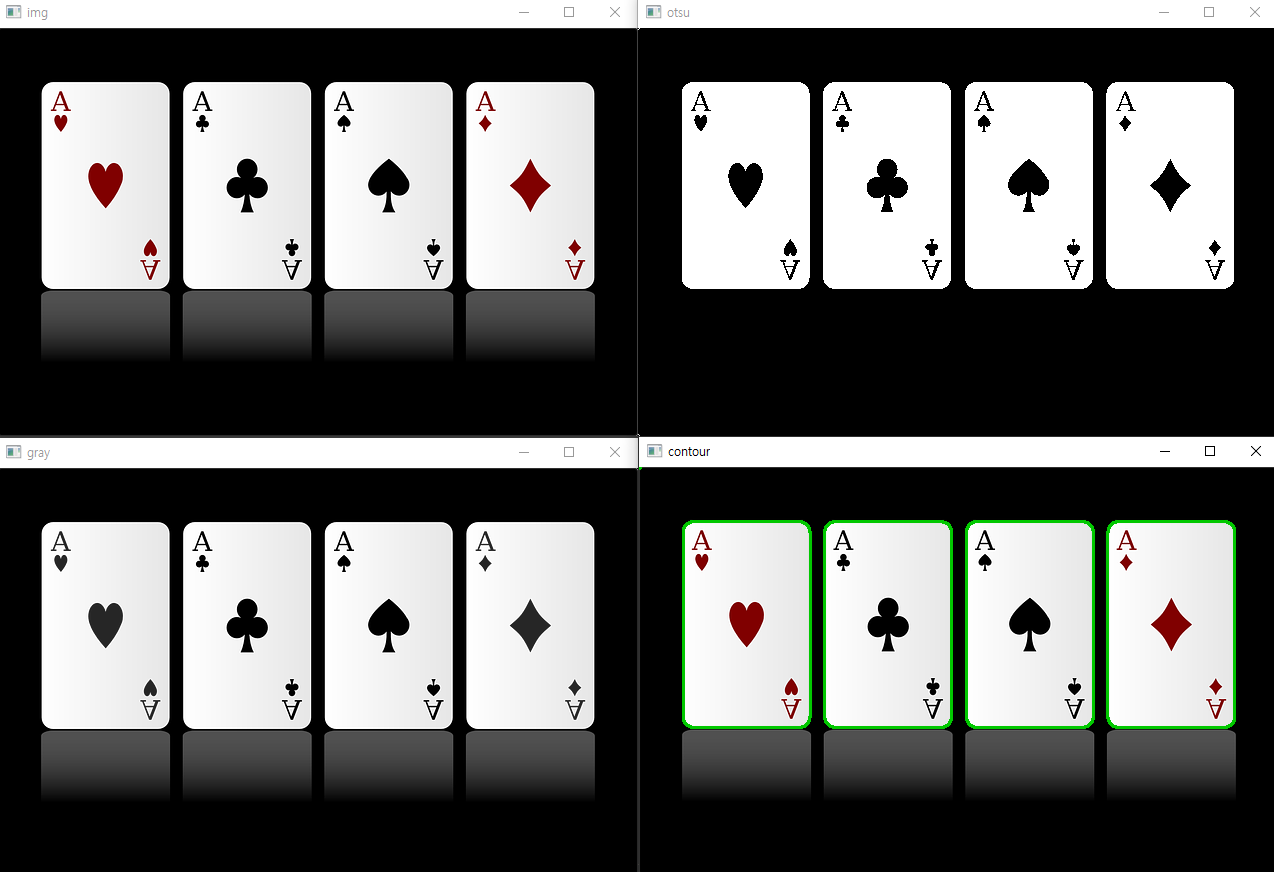
근사치 법
- CHAIN_APPROX_NONE : 모든 좌표 반환
- CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE : 꼭지점 좌표만 중복 제거하여 반환 (메모리 절약)
윤곽선 찾기 모드
- cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL : 가장 외곽의 윤곽선만 찾음
- cv2.RETR_LIST : 모든 윤곽선 찾음 (계층 정보 없음)
- cv2.RETR_TREE : 모든 윤곽선 찾음 (계층 정보를 트리 구조로 생성)
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
target_img = img.copy() # 사본 이미지
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(gray, -1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# print(hierarchy)
# print(f'총 발견 갯수 : {len(contours)}')
COLOR = (0, 200, 2) # 녹색
cv2.drawContours(target_img, contours, -1, COLOR, 2)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
cv2.imshow('otsu', otsu)
cv2.imshow('contour', target_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
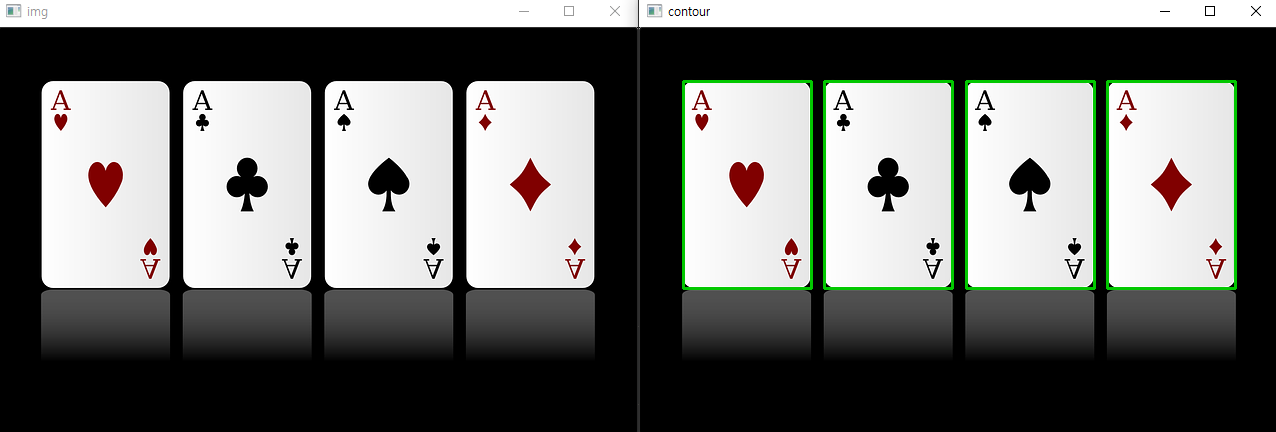
경계 사각형
윤곽선의 경계면을 둘러싸는 사각형
boundingRect()
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
target_img = img.copy() # 사본 이미지
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(gray, -1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
COLOR = (0, 200, 2) # 녹색
for cnt in contours:
x, y, width, height = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
cv2.rectangle(target_img, (x, y), (x + width, y + height), COLOR, 2) # 사각형 그리기
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('gray', gray)
cv2.imshow('otsu', otsu)
cv2.imshow('contour', target_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
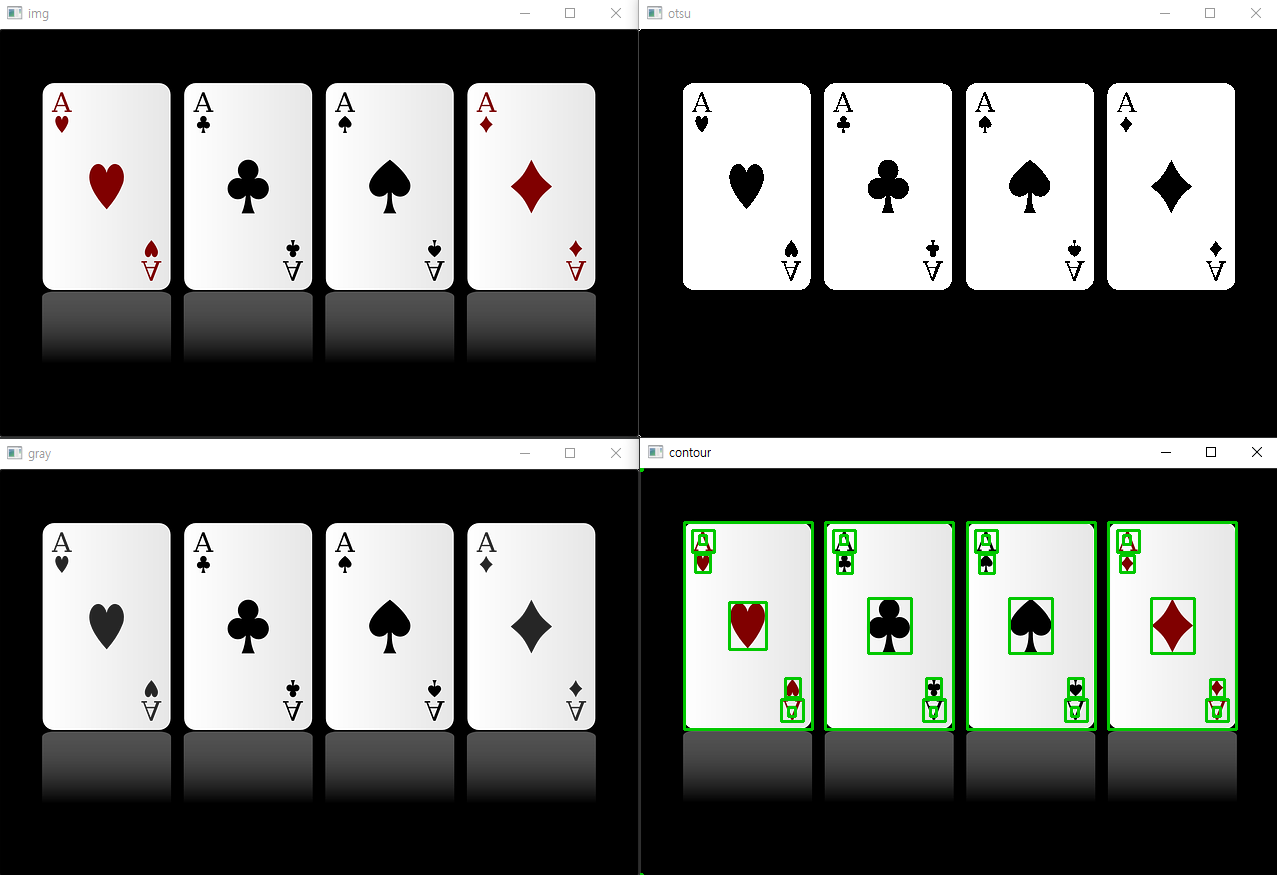
면적
contourArea()
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
target_img = img.copy() # 사본 이미지
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(gray, -1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
COLOR = (0, 200, 2) # 녹색
for cnt in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(cnt) > 25000: # 카드의 면적
x, y, width, height = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
cv2.rectangle(target_img, (x, y), (x + width, y + height), COLOR, 2)
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('contour', target_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
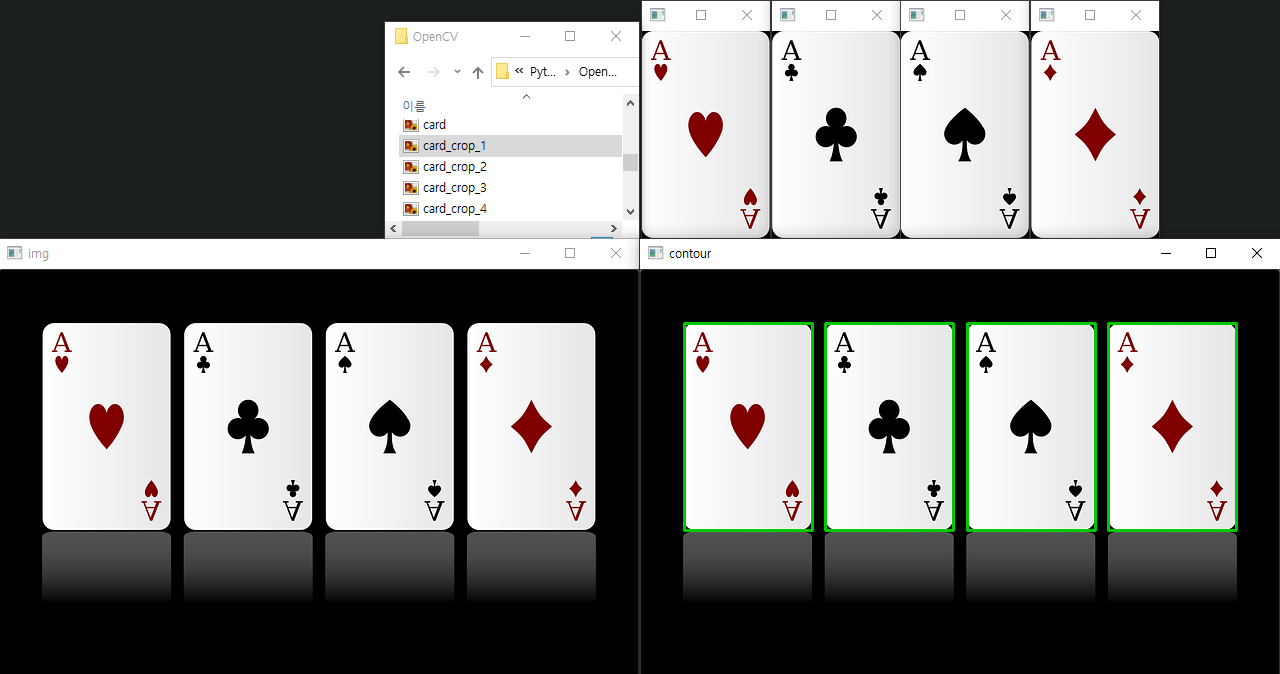
미니 프로젝트 : 개별 카드 추출해서 파일 저장
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('card.png')
target_img = img.copy()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, otsu = cv2.threshold(gray, -1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(otsu, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
COLOR = (0, 200, 2)
idx = 1
for cnt in contours:
if cv2.contourArea(cnt) > 25000:
x, y, width, height = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
cv2.rectangle(target_img, (x, y), (x + width, y + height), COLOR, 2)
crop = img[y:y+height, x:x+width]
cv2.imshow(f'card_crop_{idx}', crop)
cv2.imwrite(f'card_crop_{idx}.png', crop) # 파일 저장
idx += 1
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.imshow('contour', target_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
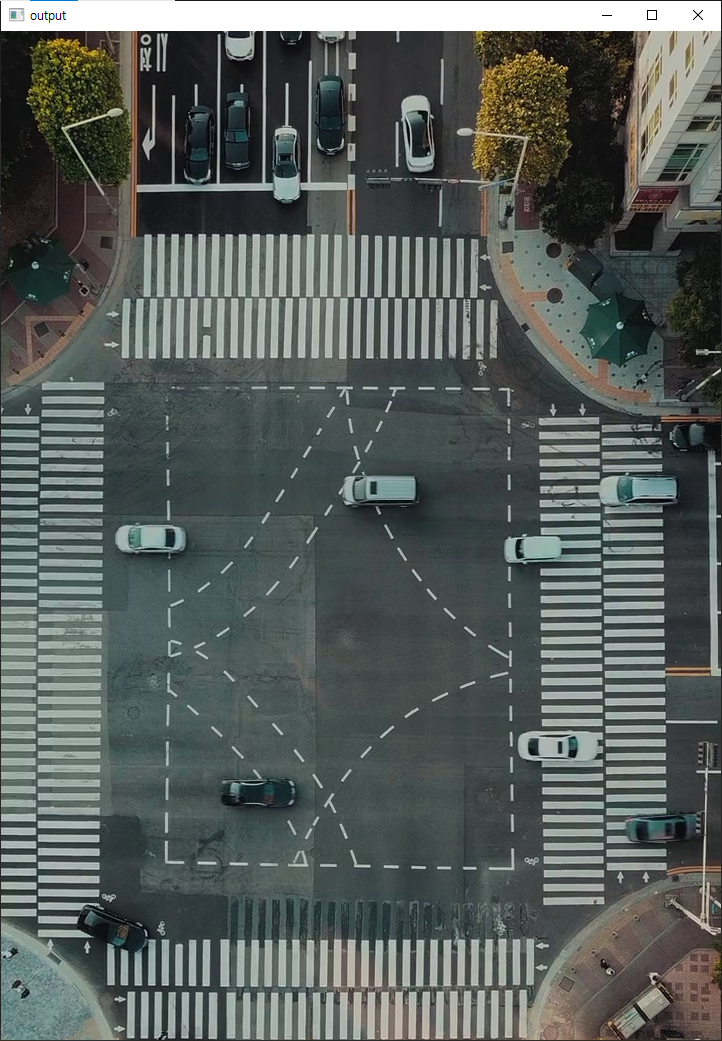
퀴즈
OpenCV를 이용하여 가로로 촬영된 영상을 세로로 회전하는 프로그램 작성
조건
- 회전: 반시계 방향으로 90도
- 재생속도(FPS): 원본의 x4
- 출력 파일명: city_output.avi(코덱:DIVX)
- 원본 파일명: city.mp4
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('city.mp4')
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'DIVX')
width = round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
height = round(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) * 4
out = cv2.VideoWriter('city_output.avi', fourcc, fps, (width, height))
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
rotate = cv2.rotate(frame, cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
out.write(rotate)
cv2.imshow('output', rotate)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):
break
out.release()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Reference
- 나도코딩: 파이썬 코딩 무료 강의 (활용편6) - OpenCV 이미지 처리
- Pexels, Tembela Bohle: 책 이미지
- Pixabay, OpenClipart-Vectors: 눈사람 이미지
- Pixabay, OpenClipart-Vectors: 카드 이미지
- Pexels, Taryn Elliott: 퀴즈 영상

댓글남기기