Python (8) - Pandas
Pandas란?
- pandas는 “python data analysis”의 약자
pandas는 정형 데이터 처리에 특화되어 있다.
- pandas 역시 다양한 머신러닝 라이브러리들에 의존성을 가지고 있다.
scikit-learn, scipy, statsmodel, tensorflow, pytorch, …
- 간단하게 생각하면, python에서 excel의 기능을 사용할 수 있게 된다.
pandas = python + excel // pandas & excel // pandas VS MS Excel
- 하지만, pandas는 numpy array를 베이스로 지원하며 파이썬과 함께 강력한 시너지를 내기 때문에, 엑셀 그 이상의 퍼포먼스를 낸다.
pandas가 Excel에 비해 고성능 데이터처리에 적합하다.

-
Pandas 라이브러리에서 기본적으로 데이터를 다루는 단위는 DataFrame이다. 흔히 알고있는 spreadsheet와 같은 개념
-
이러한 형태의 데이터는 Structured Data 또는 Panel Data 또는 Tabular Data라고 부른다.
-
pandas를 공부한다는 것은 결국 dataframe의 사용법을 익히고 활용하는 방법을 배운다는 것과 같다.
-
pandas를 잘 활용하면 대부분의 structured data를 자유자재로 다룰 수 있게 된다.
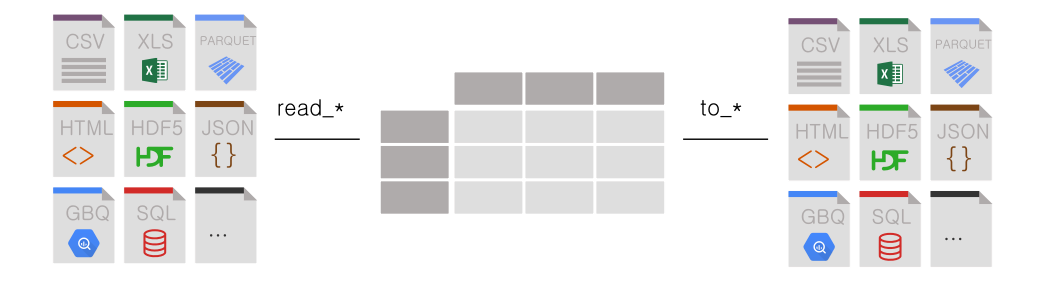
Pandas Basic
Pandas의 기본 자료구조(Series, DataFrame)
# pandas 라이브러리를 불러온다. pd를 약칭으로 사용한다.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
print(pd.__version__) # pandas version 확인
1.5.1
-
DataFrame은 2차원 테이블이고, 테이블의 한 줄(행/열)을 Series라고 한다.
-
Series의 모임이 곧, DataFrame이 된다.
# s는 1, 3, 5, np.nan, 6, 8을 원소로 가지는 pandas.Series
s = pd.Series([1, 3, 5, np.nan, 6, 8])
s
0 1.0
1 3.0
2 5.0
3 NaN
4 6.0
5 8.0
dtype: float64
- pandas는 date_range라는 함수를 통해, 날짜정보를 쉽게 생성해주는 객체도 제공한다.
# 20210101부터 6일간의 날짜 범위를 생성하는 pandas.date_range
dates = pd.date_range('20210101', periods=6)
dates
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-02', '2021-01-03', '2021-01-04',
'2021-01-05', '2021-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
# 6x4 행렬에 -1에서 1 사이의 랜덤한 숫자를 가지는 원소를 가지고, index열은 dates,
# 나머지 coulmns은 순서대로 A, B, C, D로 하는 DataFrame 생성
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6, 4), index=dates, columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
df
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | -2.460511 | -1.200258 | -0.783842 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | -1.125980 | 1.665172 | 0.789345 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 | 0.909311 |
| 2021-01-06 | 0.506280 | -0.699825 | -1.805485 | -0.639235 |
Dataframe 기초 method
# dataframe의 맨 위 다섯줄을 보여주는 head()
df.head() # default=5
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | -2.460511 | -1.200258 | -0.783842 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | -1.125980 | 1.665172 | 0.789345 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 | 0.909311 |
# 3줄
df.head(3)
# df.tail(3)
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | -2.460511 | -1.200258 | -0.783842 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
# dataframe index
df.index
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-02', '2021-01-03', '2021-01-04',
'2021-01-05', '2021-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
# dataframe columns
df.columns
Index(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'], dtype='object')
# dataframe values
df.values
array([[ 0.99572683, -2.46051099, -1.20025819, -0.78384235],
[ 1.03639362, 0.4734429 , -1.17827902, 1.73439309],
[-0.34024606, 0.003744 , 0.70652361, 0.22062538],
[ 0.00399443, -1.12598039, 1.6651719 , 0.78934461],
[ 0.16732115, 0.65711984, 0.38858045, 0.9093105 ],
[ 0.50628041, -0.69982494, -1.80548532, -0.63923458]])
# dataframe에 대한 전체적인 요약정보 (index, columns, null/not-null/dtype/memory usage)
df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
DatetimeIndex: 6 entries, 2021-01-01 to 2021-01-06
Freq: D
Data columns (total 4 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 A 6 non-null float64
1 B 6 non-null float64
2 C 6 non-null float64
3 D 6 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(4)
memory usage: 240.0 bytes
# dataframe에 대한 전체적인 통계정보
df.describe()
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 6.000000 | 6.000000 | 6.000000 | 6.000000 |
| mean | 0.394912 | -0.525335 | -0.237291 | 0.371766 |
| std | 0.553164 | 1.167203 | 1.354538 | 0.969585 |
| min | -0.340246 | -2.460511 | -1.805485 | -0.783842 |
| 25% | 0.044826 | -1.019442 | -1.194763 | -0.424270 |
| 50% | 0.336801 | -0.348040 | -0.394849 | 0.504985 |
| 75% | 0.873365 | 0.356018 | 0.627038 | 0.879319 |
| max | 1.036394 | 0.657120 | 1.665172 | 1.734393 |
# column B를 기준으로 내림차순 정렬
df.sort_values(by='B', ascending=False).head(3)
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 | 0.909311 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
DataFrame Indexing
Indexing : 데이터에서 어떤 특정 조건을 만족하는 원소를 찾는 방법.
전체 DataFrame에서 조건에 만족하는 데이터를 쉽게 찾아서 조작할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있다.
# column 이름을 이용하여 기본적인 Indexing이 가능
df["A"]
# dataframe에 바로 indexing을 사용하면, column을 찾는다. == dictionary의 indexing과 같다.
# == "key"를 indexing. == "key" == "column"
# df["2021-01-01"]
2021-01-01 0.995727
2021-01-02 1.036394
2021-01-03 -0.340246
2021-01-04 0.003994
2021-01-05 0.167321
2021-01-06 0.506280
Freq: D, Name: A, dtype: float64
# 인덱스명으로 indexing (Serise를 하나 추출) loc: location
df.loc['2021-01-01']
A 0.995727
B -2.460511
C -1.200258
D -0.783842
Name: 2021-01-01 00:00:00, dtype: float64
# 특정 위치를 통한 indexing (인덱스번호로 추출) iloc: integer location
df.iloc[2]
A -0.340246
B 0.003744
C 0.706524
D 0.220625
Name: 2021-01-03 00:00:00, dtype: float64
# dataframe에서 slicing을 이용하면 row 단위로
# 앞에서 3줄을 slicing
df[:3] # 숫자를 그냥 사용하게되면, index(양의 정수)를 이용한 slicing
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | -2.460511 | -1.200258 | -0.783842 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
# df에서 index value를 기준으로 indexing (row 단위)
# 20210102부터 20210104까지
df['2021-01-02':'2021-01-04'] # index를 이용한 slicing
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | -1.125980 | 1.665172 | 0.789345 |
# df.loc는 특정값을 기준으로 indexing (key - value)
df.loc[dates[0]] # 굳이 dates 변수를 가져오므로 좋지 못함...(리스트 형태)
A 0.995727
B -2.460511
C -1.200258
D -0.783842
Name: 2021-01-01 00:00:00, dtype: float64
# df.loc에 2차원 indexing도 가능
# [:, ["A", "B"]]의 의미는 모든 row에 대해서 columns는 A, B만 가져오라는 의미
df.loc[:, ["A", "C"]] # dataframe에서 2차원 indexing을 할 때, column들은 리스트로 넘겨줄 수 있다.
| A | C | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | -1.200258 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | -1.178279 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.706524 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | 1.665172 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.388580 |
| 2021-01-06 | 0.506280 | -1.805485 |
# slicing을 통해 특정 row중에서 columns는 A, B
df.loc['2021-01-03':'2021-01-05', ['A', 'C']]
| A | C | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.706524 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | 1.665172 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.388580 |
# 특정 row를 index값을 통한 indexing
df.loc['2021-01-02', ['A', 'B']]
A 1.036394
B 0.473443
Name: 2021-01-02 00:00:00, dtype: float64
# 2차원 리스트 indexing과 같은 원리
df.loc['2021-01-01', 'C'] # 특정 row(index)에 특정 column값.
-1.2002581918334518
# df.iloc는 정수를 이용한 indexing과 같다.(row 기준)
df.iloc[3]
A 0.003994
B -1.125980
C 1.665172
D 0.789345
Name: 2021-01-04 00:00:00, dtype: float64
df.iloc[3:5, 0:2] # df.iloc의 indexing은 numpy array의 2차원 index과 동일해진다.
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | -1.12598 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.65712 |
# slicing이 아닌 직접 리스트 형태로 기재하는 indexing
df.iloc[[1, 2, 4], [0, 3]] # filtering.
| A | D | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.909311 |
df.iloc[1:3, :]
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
df.iloc[:, 1:3] # numpy array의 2차원 indexing과 같다.
| B | C | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | -2.460511 | -1.200258 |
| 2021-01-02 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 |
| 2021-01-03 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 |
| 2021-01-04 | -1.125980 | 1.665172 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 |
| 2021-01-06 | -0.699825 | -1.805485 |
df
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | -2.460511 | -1.200258 | -0.783842 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | -1.178279 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | -0.340246 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | -1.125980 | 1.665172 | 0.789345 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 | 0.909311 |
| 2021-01-06 | 0.506280 | -0.699825 | -1.805485 | -0.639235 |
# pandas는 fancy indexing을 지원한다. (사실 numpy에서 지원하기 때문에 pandas도 지원.)
# fancy indexing이란 조건문을 통해 indexing을 할 수 있는 방법으로
# True와 False를 원소로 하는 리스트를 통해 masking하는 원리로 동작한다.
# column A에 있는 원소들중에 0보다 큰 데이터를 가져온다.
df['A'] > 0
2021-01-01 True
2021-01-02 True
2021-01-03 False
2021-01-04 True
2021-01-05 True
2021-01-06 True
Freq: D, Name: A, dtype: bool
df.loc[:, 'A'] > 0
2021-01-01 True
2021-01-02 True
2021-01-03 False
2021-01-04 True
2021-01-05 True
2021-01-06 True
Freq: D, Name: A, dtype: bool
df[df['A'] > 0]['B'] # A가 0이상인 값 중에 B값만 출력
2021-01-01 -2.460511
2021-01-02 0.473443
2021-01-04 -1.125980
2021-01-05 0.657120
2021-01-06 -0.699825
Name: B, dtype: float64
# fancy indexing
df['A'][df["A"] > 0] # chain indexing : indexing이 앞에서부터 뒤로 쭉 순서대로 적용
2021-01-01 0.995727
2021-01-02 1.036394
2021-01-04 0.003994
2021-01-05 0.167321
2021-01-06 0.506280
Name: A, dtype: float64
df[df < 0] = 0
df
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | 0.000000 | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | 0.000000 | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | 0.000000 | 1.665172 | 0.789345 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 | 0.909311 |
| 2021-01-06 | 0.506280 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
df[df > 0]
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | 0.995727 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 2021-01-02 | 1.036394 | 0.473443 | NaN | 1.734393 |
| 2021-01-03 | NaN | 0.003744 | 0.706524 | 0.220625 |
| 2021-01-04 | 0.003994 | NaN | 1.665172 | 0.789345 |
| 2021-01-05 | 0.167321 | 0.657120 | 0.388580 | 0.909311 |
| 2021-01-06 | 0.506280 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
dates = pd.date_range('20210101', periods=6)
dates
DatetimeIndex(['2021-01-01', '2021-01-02', '2021-01-03', '2021-01-04',
'2021-01-05', '2021-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6, 4), index=dates,
columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
df
| A | B | C | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | -2.043028 | 0.185646 | -2.136323 | -1.423348 |
| 2021-01-02 | -0.367051 | 0.685330 | -1.289581 | 0.697019 |
| 2021-01-03 | 0.554580 | 0.839659 | 2.055305 | -1.228955 |
| 2021-01-04 | 2.711900 | 0.242401 | -0.590835 | 0.813524 |
| 2021-01-05 | 1.220737 | 0.362214 | 2.217728 | 0.350189 |
| 2021-01-06 | -1.570875 | -1.106490 | -0.866496 | 1.076941 |
df2 = df.copy() # dataframe 하나를 복사
# dataframe은 dictionary와 비슷한 방식으로 assignment가 가능하다.
# df에 ['one', 'one','two','three','four','three'] 리스트를 column의 value로 하는 column E를 추가한다.
df2['E'] = ['one', 'one','two','three','four','three'] # 만약 이미 column E가 존재한다면 update
df2
| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-01 | -2.043028 | 0.185646 | -2.136323 | -1.423348 | one |
| 2021-01-02 | -0.367051 | 0.685330 | -1.289581 | 0.697019 | one |
| 2021-01-03 | 0.554580 | 0.839659 | 2.055305 | -1.228955 | two |
| 2021-01-04 | 2.711900 | 0.242401 | -0.590835 | 0.813524 | three |
| 2021-01-05 | 1.220737 | 0.362214 | 2.217728 | 0.350189 | four |
| 2021-01-06 | -1.570875 | -1.106490 | -0.866496 | 1.076941 | three |
# df.isin은 해당 value들이 들어있는 row에 대해선 True를 가지는 Series를 리턴한다.
df2['E'].isin(['two','four'])
2021-01-01 False
2021-01-02 False
2021-01-03 True
2021-01-04 False
2021-01-05 True
2021-01-06 False
Freq: D, Name: E, dtype: bool
df2[df2['E'].isin(['two','four'])]
| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-01-03 | 0.554580 | 0.839659 | 2.055305 | -1.228955 | two |
| 2021-01-05 | 1.220737 | 0.362214 | 2.217728 | 0.350189 | four |
외부 데이터 읽고 쓰기
# data 폴더에 있는 iris.csv를 불러오자.
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("data/Iris.csv")
data
| Id | SepalLengthCm | SepalWidthCm | PetalLengthCm | PetalWidthCm | Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 1 | 2 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 2 | 3 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 3 | 4 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| 4 | 5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | Iris-setosa |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 145 | 146 | 6.7 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.3 | Iris-virginica |
| 146 | 147 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 1.9 | Iris-virginica |
| 147 | 148 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.0 | Iris-virginica |
| 148 | 149 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 5.4 | 2.3 | Iris-virginica |
| 149 | 150 | 5.9 | 3.0 | 5.1 | 1.8 | Iris-virginica |
150 rows × 6 columns
# Species column을 숫자로 바꿔보자.
set(data["Species"])
{'Iris-setosa', 'Iris-versicolor', 'Iris-virginica'}
data.loc[data["Species"] == "Iris-setosa", "Species"] = 0
data.loc[data["Species"] == "Iris-versicolor", "Species"] = 1
data.loc[data["Species"] == "Iris-virginica", "Species"] = 2
data
| Id | SepalLengthCm | SepalWidthCm | PetalLengthCm | PetalWidthCm | Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 3 | 4 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0 |
| 4 | 5 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 145 | 146 | 6.7 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 146 | 147 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 1.9 | 2 |
| 147 | 148 | 6.5 | 3.0 | 5.2 | 2.0 | 2 |
| 148 | 149 | 6.2 | 3.4 | 5.4 | 2.3 | 2 |
| 149 | 150 | 5.9 | 3.0 | 5.1 | 1.8 | 2 |
150 rows × 6 columns
# 바꾼 Dataframe을 Iris_edited.csv 로 저장하자.
data.to_csv("data/Iris_edited.csv")
# 다른 파일도 불러오자.
import pandas as pd
data2 = pd.read_csv("data/kaggle_survey_2020_responses.csv", low_memory=False)
# 박사 학위 소지자들만 골라보자.
phds = data2[data2.iloc[:, 4] == "Doctoral degree"]
phds
| Time from Start to Finish (seconds) | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7_Part_1 | Q7_Part_2 | Q7_Part_3 | ... | Q35_B_Part_2 | Q35_B_Part_3 | Q35_B_Part_4 | Q35_B_Part_5 | Q35_B_Part_6 | Q35_B_Part_7 | Q35_B_Part_8 | Q35_B_Part_9 | Q35_B_Part_10 | Q35_B_OTHER | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1838 | 35-39 | Man | Colombia | Doctoral degree | Student | 5-10 years | Python | R | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 9 | 762 | 35-39 | Man | Germany | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 5-10 years | Python | NaN | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 12 | 742 | 35-39 | Man | United States of America | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 1-2 years | NaN | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 21 | 3313 | 22-24 | Woman | India | Doctoral degree | Statistician | 3-5 years | NaN | R | SQL | ... | Weights & Biases | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 33 | 459 | 30-34 | Man | Other | Doctoral degree | Machine Learning Engineer | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 20003 | 917 | 30-34 | Man | Colombia | Doctoral degree | Software Engineer | 5-10 years | Python | NaN | SQL | ... | Weights & Biases | Comet.ml | Sacred + Omniboard | TensorBoard | Guild.ai | Polyaxon | Trains | Domino Model Monitor | NaN | NaN |
| 20005 | 406 | 30-34 | Man | Italy | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 20007 | 487 | 45-49 | Man | United States of America | Doctoral degree | Software Engineer | 20+ years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 20011 | 375 | 40-44 | Man | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern I... | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 5-10 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 20020 | 611 | 25-29 | Prefer not to say | Germany | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
2302 rows × 355 columns
# 박사 학위 소지자들에 대한 정보만 kaggle_survey_2020_phd.csv로 다시 저장하자.
phds.to_csv("data/kaggle_survey_2020_phd.csv")
# (OPTIONAL) 박사 학위 소지자이면서, 대한민국 국적을 가진 사람들을 뽑아보자.
data2[(data2["Q4"] == "Doctoral degree") & (data2["Q3"].isin(["Republic of Korea", "South Korea"]))]
| Time from Start to Finish (seconds) | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7_Part_1 | Q7_Part_2 | Q7_Part_3 | ... | Q35_B_Part_2 | Q35_B_Part_3 | Q35_B_Part_4 | Q35_B_Part_5 | Q35_B_Part_6 | Q35_B_Part_7 | Q35_B_Part_8 | Q35_B_Part_9 | Q35_B_Part_10 | Q35_B_OTHER | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 557 | 639 | 30-34 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 3-5 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1246 | 592 | 35-39 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Other | < 1 years | NaN | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1566 | 10700 | 45-49 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1936 | 475 | 30-34 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Business Analyst | I have never written code | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | Weights & Biases | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | Domino Model Monitor | NaN | NaN |
| 2521 | 908 | 55-59 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | R | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 4144 | 385 | 30-34 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 5-10 years | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 5313 | 738 | 30-34 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 3-5 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 5649 | 933 | 25-29 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 5897 | 201039 | 25-29 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 3-5 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 6459 | 6528 | 25-29 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | I have never written code | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 6827 | 872 | 30-34 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Machine Learning Engineer | 3-5 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | Weights & Biases | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 6932 | 637 | 30-34 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 5-10 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 7479 | 727 | 40-44 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Data Analyst | 5-10 years | NaN | R | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 7902 | 236 | 45-49 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Product/Project Manager | < 1 years | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 9135 | 626 | 25-29 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 5-10 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 9236 | 716 | 25-29 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 3-5 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 9303 | 3560 | 35-39 | Woman | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | R | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 9826 | 1565 | 60-69 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 3-5 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 10473 | 464 | 40-44 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Statistician | 5-10 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 10905 | 779 | 45-49 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 5-10 years | NaN | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 11224 | 510 | 35-39 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | < 1 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 11601 | 75444 | 35-39 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 11958 | 161 | 40-44 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Machine Learning Engineer | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 12029 | 131 | 60-69 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Currently not employed | 20+ years | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 12084 | 1527 | 50-54 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 3-5 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 12191 | 707 | 35-39 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 12537 | 2998 | 25-29 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 5-10 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 12999 | 458 | 25-29 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 13349 | 947 | 25-29 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Statistician | 3-5 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 14580 | 658 | 45-49 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 14655 | 892 | 25-29 | Woman | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 5-10 years | Python | NaN | SQL | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | Trains | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 15537 | 289 | 30-34 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Student | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 15793 | 1162 | 35-39 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 10-20 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 16583 | 280 | 40-44 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Currently not employed | 10-20 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 16643 | 1045 | 55-59 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Product/Project Manager | < 1 years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | TensorBoard | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 17400 | 635 | 45-49 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Software Engineer | 20+ years | Python | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 17616 | 1166 | 50-54 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Research Scientist | 1-2 years | NaN | R | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 17927 | 652 | 30-34 | Man | South Korea | Doctoral degree | Machine Learning Engineer | < 1 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | None | NaN |
| 19867 | 708 | 25-29 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Data Scientist | 3-5 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 19990 | 455 | 25-29 | Man | Republic of Korea | Doctoral degree | Machine Learning Engineer | 5-10 years | Python | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
40 rows × 355 columns
Reference
- 이 포스트는 SeSAC 인공지능 SW 개발자 양성 과정 - 나예진 강사님의 강의내용을 정리한 것입니다.
- pandas: What kind of data does pandas handle?
- pandas: How do I read and write tabular data?
- SAURABH SINGH: Iris.csv
- kaggle: 2020 Kaggle ML & DS Survey

댓글남기기